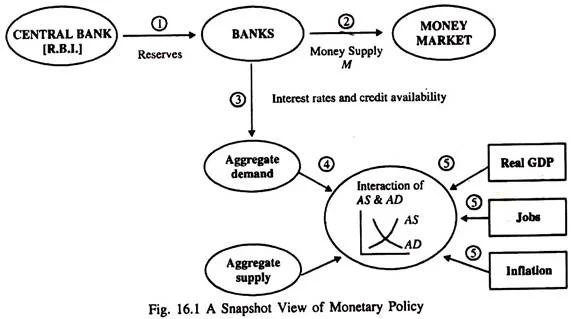
Central banks play a crucial role in shaping the economy through their monetary policy. By controlling the money supply, interest rates, and inflation, central banks have the power to influence economic growth, employment, and price stability. Through their decisions, central banks can impact the overall health of the economy, making them key players in the financial system. Additionally, central banks also act as lenders of last resort and regulate the banking industry, further shaping the economic landscape.
Monetary policy, which is set by central banks, directly impacts the economy by influencing borrowing and spending behavior. Interest rates, liquidity, and credit availability are some of the tools central banks use to control the money supply and regulate inflation. These policies also affect exchange rates, investment decisions, and the overall level of economic activity. As a result, the decisions made by central banks have far-reaching effects on businesses, consumers, and financial markets.
The Role of Central Banks in the Economy
Central banks play a crucial role in shaping the economy through their monetary policy decisions. They are responsible for controlling the money supply, interest rates, and inflation, which in turn influence economic growth, employment, and overall price stability. By adjusting these key factors, central banks can help steer the economy towards sustainable growth and mitigate the impact of economic downturns.
Additionally, central banks also serve as lenders of last resort, providing liquidity to financial institutions during times of crisis to prevent widespread banking panics. This function helps maintain stability in the financial system and supports the smooth functioning of the economy.
Monetary Policy Tools and Instruments
Central banks employ various tools and instruments to implement monetary policy. These include open market operations, where they buy or sell government securities to influence the money supply and interest rates. They also use reserve requirements to regulate the amount of funds that banks must hold in reserve, affecting their ability to lend. Additionally, central banks can directly set short-term interest rates, impacting borrowing costs for businesses and consumers.
Furthermore, central banks can use unconventional monetary policy measures, such as quantitative easing, to provide additional stimulus to the economy during periods of severe economic stress. These tools are carefully deployed to achieve specific economic objectives, such as controlling inflation or stimulating economic activity.
Inflation Targeting and Price Stability
One of the primary goals of many central banks is to maintain price stability by controlling inflation. Central banks often use inflation targeting as a framework for conducting monetary policy, setting a specific inflation target and adjusting their policy measures to keep inflation within the desired range. By anchoring inflation expectations, central banks can create a more predictable and stable environment for businesses and consumers to make long-term economic decisions.
Price stability is essential for promoting sustainable economic growth, as high or erratic inflation can erode the purchasing power of money, disrupt investment decisions, and lead to economic inefficiencies. Through their monetary policy actions, central banks aim to strike a balance that supports stable prices while also fostering robust economic activity.
Exchange Rate Management
Central banks often play a role in managing exchange rates, especially in countries with floating exchange rate regimes. By buying or selling their own currency in the foreign exchange market, central banks can influence the value of their currency relative to others. This can have implications for international trade, inflation, and overall economic competitiveness.
Additionally, central banks may use exchange rate policies to achieve broader economic objectives, such as supporting export-led growth or maintaining external balance. However, managing exchange rates can be a complex and contentious issue, as it involves balancing domestic economic priorities with global market dynamics and potential spillover effects.
Financial Stability and Regulation
Central banks also play a critical role in promoting financial stability and regulating the banking sector. They oversee banks’ operations, set prudential regulations, and conduct stress tests to ensure the resilience of the financial system. By monitoring potential risks and vulnerabilities, central banks aim to prevent financial crises and safeguard the overall health of the banking industry.
Furthermore, central banks may act as the lender of last resort during financial turmoil, providing emergency funding to banks to prevent systemic collapse. This function is essential for maintaining confidence in the financial system and averting widespread economic disruptions.
Communication and Transparency
Effective communication and transparency are vital aspects of central bank operations. Central banks regularly communicate their policy decisions, outlook on the economy, and the rationale behind their actions to the public and financial markets. Clear and transparent communication builds credibility and trust, helping guide market expectations and reduce uncertainty.
Moreover, central banks often provide forward guidance, signaling their intended policy path to help businesses and investors make informed decisions. By managing expectations and providing clarity on future policy actions, central banks can enhance the effectiveness of their monetary policy measures.
Challenges and Trade-Offs in Monetary Policy
Central banks face various challenges and trade-offs when conducting monetary policy. For example, they must balance the objectives of price stability, full employment, and sustainable economic growth, which may require making difficult choices between conflicting goals. Additionally, central banks must navigate external shocks, such as changes in global economic conditions or geopolitical events, which can complicate their policy decisions.
Furthermore, unconventional monetary policy measures, such as quantitative easing, can have unintended consequences, such as asset price inflation or distortions in financial markets. Central banks must carefully assess the potential risks and side effects of such measures while pursuing their policy objectives.
Global Coordination and Spillover Effects
Given the interconnected nature of the global economy, central banks often coordinate their policy actions to address common challenges and mitigate spillover effects. International cooperation among central banks can help manage exchange rate volatility, address liquidity shortages, and tackle cross-border financial risks. However, coordinating policies across different jurisdictions can be complex and may require navigating divergent economic conditions and policy priorities.
Spillover effects from one country’s monetary policy actions to others can create challenges for central banks, as changes in global financial conditions and capital flows can impact domestic economic and financial stability. Central banks must carefully assess the potential spillover effects of their policy decisions and consider the broader implications for the international economy.
Adapting to Technological and Economic Trends
Central banks must continuously adapt to technological advancements and evolving economic trends to effectively conduct monetary policy. The rise of digital currencies, fintech innovation, and changes in payment systems present new challenges and opportunities for central banks in managing the money supply and financial stability. Additionally, demographic shifts, climate change, and globalization can influence economic dynamics, requiring central banks to reassess their policy frameworks and tools.
As economic landscapes evolve, central banks may need to explore new policy approaches and regulatory measures to address emerging risks and support sustainable economic development. This adaptability is essential for central banks to fulfill their mandate of promoting monetary and financial stability in a rapidly changing world.
Accountability and Independence
Central banks operate with a degree of independence to insulate monetary policy decisions from short-term political pressures and ensure credibility and effectiveness. However, this independence is accompanied by the responsibility to be accountable to the public and policymakers. Central banks often provide regular reports, testimonies, and assessments of their policy actions, allowing for scrutiny and evaluation of their performance.
Accountability mechanisms help uphold transparency and public trust in central bank operations, fostering a more predictable and credible policy environment. At the same time, central banks must navigate the delicate balance between independence and accountability to fulfill their mandate while remaining responsive to the broader economic and societal goals.
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Regulating money supply | Central banks control the money supply to achieve economic goals such as price stability and full employment. |
| Setting interest rates | By adjusting interest rates, central banks can influence borrowing, spending, and investment in the economy. |
| Supervising financial institutions | Central banks oversee banks and other financial institutions to ensure stability and prevent financial crises. |
| Managing foreign exchange reserves | Central banks manage foreign exchange reserves to stabilize exchange rates and support international trade. |
conclusıon
The Role Of Central Banks: How Monetary Policy Shapes The Economy konusu, merkez bankalarının para politikası aracılığıyla ekonomiyi nasıl şekillendirdiğini açıklamaktadır. Merkez bankaları, para arzını düzenleyerek, faiz oranlarını belirleyerek, finansal kurumları denetleyerek ve döviz rezervlerini yöneterek ekonomik istikrarı ve büyümeyi desteklemektedir.