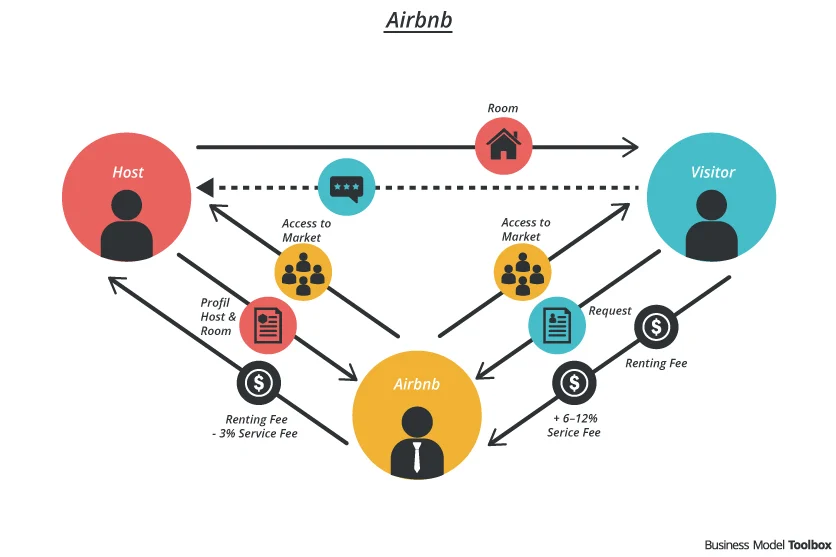
The Sharing Economy, characterized by companies like Airbnb and Uber, has been disrupting traditional industries by offering alternative ways of accessing goods and services. This new economic model allows individuals to rent out their properties or offer transportation services, creating a more efficient use of resources and providing a source of income for individuals. The Sharing Economy is reshaping the way people travel, find accommodation, and access transportation, challenging the traditional business models in these industries. Companies like Airbnb and Uber are at the forefront of this movement, changing the way people think about ownership and consumption.
As the Sharing Economy continues to gain momentum, it is revolutionizing the way people think about travel, accommodation, and transportation. This new economic model not only provides consumers with more options and flexibility, but also has the potential to reduce waste and promote sustainability. The rise of platforms like Airbnb and Uber has sparked discussions about the future of work, the concept of ownership, and the impact of technology on traditional industries. The disruptive nature of the Sharing Economy has led to debates about regulation, consumer trust, and the overall impact on society. These companies are paving the way for a new era of collaborative consumption, challenging the status quo and redefining the way we access goods and services.
The Rise of the Sharing Economy
The sharing economy, also known as the collaborative economy, is a socio-economic system built around the sharing of resources, often facilitated by technology platforms. Companies like Airbnb and Uber have disrupted traditional industries by enabling individuals to monetize their assets, such as their homes or cars, by renting them out to others. This shift has transformed the way people think about ownership and consumption, leading to a more sustainable and efficient use of resources.
One of the key drivers of the sharing economy is the desire for flexibility and convenience. By leveraging technology, individuals can easily access and offer a wide range of goods and services on a peer-to-peer basis. This has created new opportunities for both providers and consumers, allowing for greater choice, affordability, and personalized experiences.
Impact on Traditional Industries
The rise of companies like Airbnb and Uber has had a significant impact on traditional industries such as hospitality and transportation. Established players in these sectors have had to adapt to the new competitive landscape, facing challenges from these disruptive platforms that offer alternative, often more affordable options for consumers. This has led to increased innovation and a rethinking of business models within these industries.
Furthermore, the sharing economy has also sparked regulatory and legal debates, as traditional industries and local governments grapple with the implications of these new, decentralized business models. Questions around safety, taxation, and employment practices have arisen, prompting discussions on how to effectively regulate and integrate these innovative platforms into existing frameworks.
Empowerment of Individuals
One of the most notable impacts of the sharing economy is the empowerment of individuals to become micro-entrepreneurs. Platforms like Airbnb and Etsy allow people to turn their homes and creative talents into sources of income, bypassing traditional gatekeepers and middlemen. This has democratized access to the market and provided opportunities for individuals to showcase their unique offerings.
Additionally, the sharing economy has enabled greater economic participation for marginalized groups, such as those in rural areas or with limited access to traditional employment opportunities. By leveraging the reach of online platforms, individuals can tap into a global market and connect with a diverse range of customers, thereby reducing barriers to entry and expanding economic inclusion.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Another key aspect of the sharing economy is its potential to promote sustainability and reduce environmental impact. By maximizing the use of existing resources, such as idle cars or vacant living spaces, these platforms contribute to a more efficient allocation of assets and a reduction in overall waste. This can lead to a smaller carbon footprint and less strain on the environment.
Furthermore, the sharing economy encourages the concept of access over ownership, promoting a shift towards a more circular economy where goods are reused and shared, rather than being constantly produced and discarded. This mindset aligns with the principles of conservation and responsible consumption, offering a more sustainable approach to meeting consumer needs.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its many benefits, the sharing economy has also faced criticisms and challenges. One common concern is the potential for negative impacts on traditional employment, as the rise of gig economy platforms may lead to job insecurity and a lack of labor protections for workers. This has sparked debates around the classification of workers and the need for updated labor regulations.
Additionally, issues related to trust and safety have been raised, as the decentralized nature of the sharing economy can make it difficult to ensure consistent standards and accountability across different transactions. This has prompted calls for enhanced transparency and mechanisms for resolving disputes in order to build and maintain trust within these platforms.
Future of the Sharing Economy
Looking ahead, the sharing economy is expected to continue evolving and expanding into new sectors and geographic regions. As technology advances and consumer behaviors change, we can anticipate the emergence of innovative platforms that facilitate sharing and collaboration in areas such as healthcare, education, and more. This ongoing transformation will likely shape the way we interact with goods and services in the years to come.
Furthermore, the sharing economy is likely to influence public policy and regulatory frameworks, as governments seek to strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring the protection of consumers and workers. Collaboration between industry stakeholders and policymakers will be crucial in navigating these complexities and unlocking the full potential of the sharing economy while addressing its associated challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rise of companies like Airbnb and Uber has ushered in a new era of economic activity, characterized by the sharing and utilization of underutilized resources. This shift has not only disrupted traditional industries but has also empowered individuals, promoted sustainability, and presented both opportunities and challenges for society at large. As the sharing economy continues to shape our economic landscape, it will be important to consider its broader implications and work towards creating a balanced and inclusive ecosystem for all participants.
“`html
| Companies | Industry | Disruption |
|---|---|---|
| Airbnb | Hospitality | Enabling individuals to rent out their properties, disrupting traditional hotels |
| Uber | Transportation | Connecting riders with drivers, challenging traditional taxi services |
conclusıon
The sharing economy, represented by companies like Airbnb and Uber, is reshaping traditional industries by enabling peer-to-peer transactions and challenging established business models.
“`