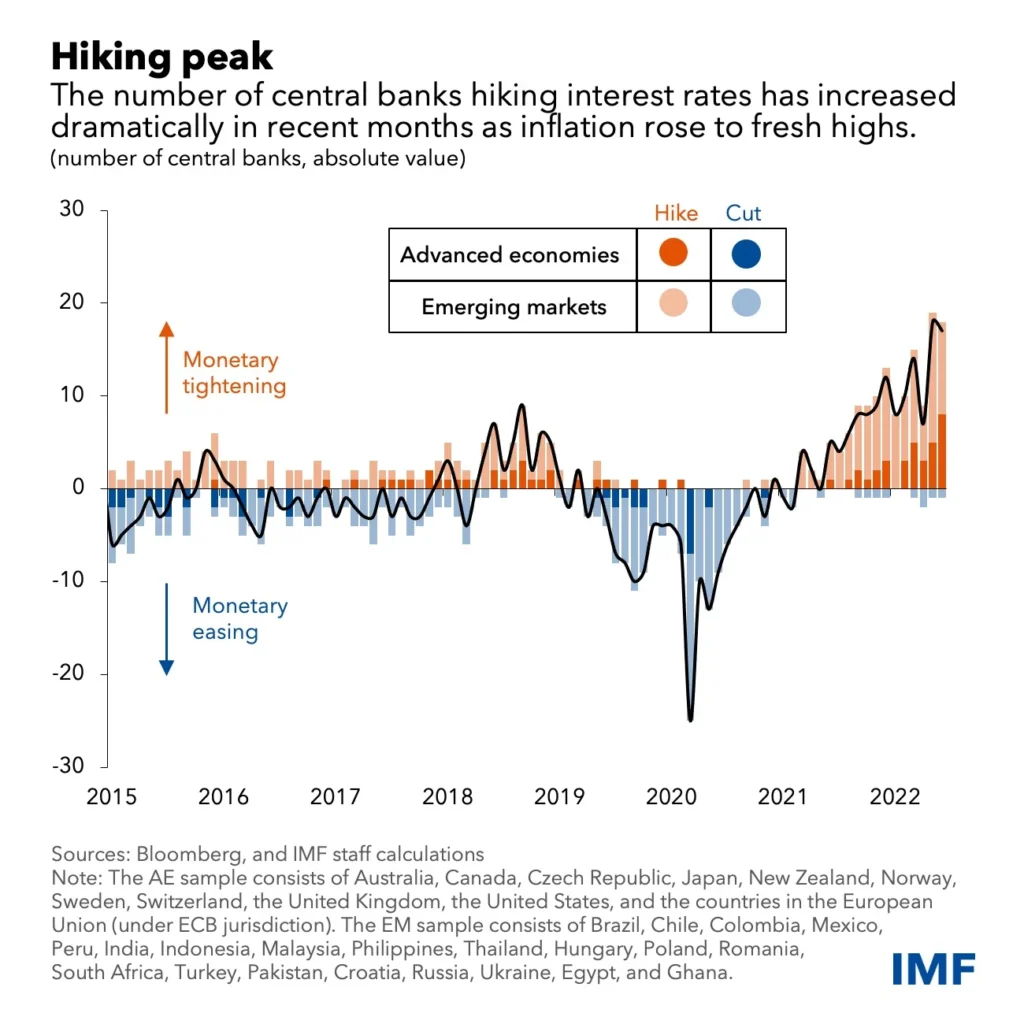
Central bank policies have a significant impact on the economy, particularly in terms of interest rates and inflation. The decisions made by central banks regarding monetary policy can directly influence the cost of borrowing and lending, which in turn affects consumer spending, investment, and overall economic activity. Additionally, central bank policies play a crucial role in controlling inflation, as they can use interest rates to manage the money supply and keep inflation in check. Therefore, it is essential to closely monitor the actions of central banks and their impact on interest rates and inflation in order to understand the broader economic environment.
The policies implemented by central banks have a profound effect on the economy, particularly in relation to the cost of borrowing and lending, as well as the overall level of prices. The decisions made by central banks regarding monetary policy can directly influence consumer behavior, business investment, and the overall performance of the economy. Furthermore, central bank policies are crucial in maintaining price stability and controlling the rate of inflation, as they have the ability to use interest rates as a tool to manage the money supply. Consequently, it is important to closely analyze the actions of central banks and their influence on interest rates and inflation in order to comprehend the broader economic landscape.
1. The Role of Central Banks in Setting Interest Rates
Central banks play a crucial role in setting interest rates, which have a significant impact on the economy. When the central bank raises interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive, leading to a decrease in consumer spending and business investment. This can help to control inflation by reducing aggregate demand. On the other hand, when the central bank lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, stimulating consumer spending and business investment, which can help to boost economic growth. Therefore, the central bank’s decisions regarding interest rates have a direct impact on the overall economic activity.
Furthermore, central banks use interest rates as a tool to achieve their monetary policy objectives. By adjusting interest rates, central banks can influence the money supply, control inflation, and stabilize the currency. For example, if the central bank aims to stimulate economic growth, it may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing and spending. Conversely, if the central bank aims to curb inflation, it may raise interest rates to reduce borrowing and spending. In this way, central banks use interest rates as a mechanism to achieve their macroeconomic goals.
2. The Link Between Interest Rates and Consumer Spending
Interest rates have a direct impact on consumer spending. When interest rates are low, borrowing costs decrease, making it more affordable for consumers to take out loans for big-ticket items such as homes, cars, and appliances. This can lead to an increase in consumer spending, as individuals are more willing to make purchases on credit. Additionally, lower interest rates can also lead to higher disposable income, as mortgage and loan payments decrease, leaving consumers with more money to spend on other goods and services.
Conversely, when interest rates are high, borrowing costs increase, making it more expensive for consumers to take out loans. This can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, as individuals are less willing to incur high interest expenses. Higher interest rates can also lead to lower disposable income, as mortgage and loan payments rise, leaving consumers with less money to spend on other goods and services. Therefore, the level of interest rates directly influences the behavior of consumers and their overall spending patterns.
3. The Impact of Interest Rates on Business Investment
Interest rates also have a significant impact on business investment. When interest rates are low, the cost of borrowing for businesses decreases, making it more attractive for them to take out loans to finance expansion, capital expenditures, and research and development. This can lead to an increase in business investment, as companies are more willing to undertake new projects and initiatives. Additionally, lower interest rates can lead to higher profitability for businesses, as the cost of servicing debt decreases.
Conversely, when interest rates are high, the cost of borrowing for businesses increases, making it less attractive for them to take out loans. This can lead to a decrease in business investment, as companies are less willing to incur high interest expenses to finance new projects. Higher interest rates can also lead to lower profitability for businesses, as the cost of servicing debt rises. Therefore, the level of interest rates directly influences the investment decisions of businesses and their overall growth prospects.
4. The Relationship Between Interest Rates and Inflation
There is a strong relationship between interest rates and inflation. When central banks raise interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive, leading to a decrease in consumer spending and business investment. This reduction in aggregate demand can help to control inflation, as prices are less likely to rise when there is less spending in the economy. Therefore, higher interest rates are often used as a tool to combat inflationary pressures by cooling down economic activity.
Conversely, when central banks lower interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, stimulating consumer spending and business investment. This can lead to an increase in aggregate demand, which may put upward pressure on prices and contribute to inflation. Therefore, lower interest rates are often used as a tool to stimulate economic growth, but there is also a risk of fueling inflation if the economy becomes overheated. As a result, central banks must carefully consider the impact of interest rate changes on inflation when formulating their monetary policy decisions.
5. The Role of Central Banks in Controlling Inflation
Central banks play a crucial role in controlling inflation through their monetary policy decisions. By adjusting interest rates and influencing the money supply, central banks can effectively manage inflationary pressures in the economy. When inflation is rising above the target level, central banks may raise interest rates to reduce borrowing and spending, thereby cooling down economic activity and dampening price increases. This can help to bring inflation back to the desired level and maintain price stability.
Conversely, when inflation is below the target level or the economy is experiencing deflationary pressures, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending, thereby boosting economic activity and preventing a prolonged period of falling prices. By using interest rates as a tool to influence inflation, central banks aim to achieve a balance between supporting economic growth and maintaining price stability. This requires careful monitoring of economic indicators and a proactive approach to managing monetary policy.
6. The Impact of Central Bank Communication on Interest Rates
Central bank communication plays a crucial role in shaping market expectations and influencing interest rates. When central bank officials communicate their monetary policy decisions, outlook for the economy, and inflation expectations, it can have a direct impact on financial markets and interest rate movements. For example, if central bank officials signal a potential interest rate hike in the future, it can lead to an immediate increase in market interest rates as investors adjust their expectations and pricing of future borrowing costs.
Conversely, if central bank officials signal a potential interest rate cut or a dovish stance on monetary policy, it can lead to a decrease in market interest rates as investors anticipate lower borrowing costs in the future. Therefore, central bank communication can influence the behavior of market participants, leading to changes in interest rates that can have broader implications for consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic activity. As a result, central bank transparency and clarity in communication are essential for shaping market expectations and maintaining stability in interest rate movements.
7. The Global Impact of Central Bank Policies on Interest Rates
Central bank policies and interest rate decisions can have a global impact, as they influence capital flows, exchange rates, and financial market conditions across borders. When a major central bank, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank, changes its interest rates, it can lead to spillover effects on other economies and financial markets. For example, a decision to raise interest rates by a major central bank can attract foreign capital seeking higher returns, leading to an appreciation of the domestic currency and potential challenges for export-oriented industries.
Conversely, a decision to lower interest rates by a major central bank can lead to a depreciation of the domestic currency, making exports more competitive in international markets and potentially boosting economic growth. However, it can also lead to capital outflows from the domestic economy as investors seek higher returns elsewhere. Therefore, central bank policies and interest rate decisions have far-reaching implications for global financial stability and can influence the interconnectedness of economies in an increasingly integrated world.
8. The Impact of Unconventional Monetary Policies on Interest Rates
In response to the global financial crisis of 2008 and subsequent economic challenges, central banks have employed unconventional monetary policies to influence interest rates and support economic recovery. These unconventional policies, such as quantitative easing and forward guidance, have involved large-scale purchases of financial assets and explicit commitments to keep interest rates at low levels for an extended period. By implementing these measures, central banks have aimed to lower long-term interest rates, stimulate borrowing and spending, and support economic growth.
However, the impact of unconventional monetary policies on interest rates has been a subject of debate. While these measures have helped to lower borrowing costs and support asset prices, they have also raised concerns about potential distortions in financial markets, excessive risk-taking, and the effectiveness of prolonged low interest rates. As central banks navigate the challenges of normalizing monetary policy after a period of unconventional measures, the impact of these policies on interest rates and their broader implications for the economy continue to be closely monitored and analyzed.
9. The Role of Inflation Targeting in Central Bank Policies
Inflation targeting is a common framework used by central banks to guide their monetary policy decisions and communicate their policy objectives to the public. Under an inflation targeting regime, central banks set a specific target for the annual inflation rate and adjust their monetary policy tools, including interest rates, to achieve this target. By focusing on controlling inflation within a predetermined range, central banks aim to provide clarity and transparency about their policy intentions and contribute to macroeconomic stability.
Through inflation targeting, central banks seek to anchor inflation expectations, which can influence wage negotiations, price-setting behavior, and long-term financial planning. By maintaining credibility in their commitment to achieving the inflation target, central banks aim to reduce uncertainty and promote stable economic conditions. However, the effectiveness of inflation targeting as a policy framework is subject to ongoing evaluation, as central banks adapt to evolving economic dynamics and global challenges that may impact inflation dynamics and the transmission mechanisms of monetary policy.
10. The Challenges of Achieving Monetary Policy Objectives Through Interest Rates
Central banks face a range of challenges in achieving their monetary policy objectives through interest rate decisions. In a dynamic and interconnected global economy, central banks must navigate uncertainties related
| Central Bank Policy | Impact on Interest Rates | Impact on Inflation |
|---|---|---|
| Tightening Monetary Policy | Raises interest rates to reduce borrowing and spending | Reduces inflation by slowing down economic growth |
| Easing Monetary Policy | Lowers interest rates to encourage borrowing and spending | May increase inflation by stimulating economic growth |
Central bank policies have a significant impact on interest rates and inflation. By adjusting monetary policy, central banks can influence borrowing and spending, which in turn affects economic growth and inflation. Tightening monetary policy raises interest rates and reduces inflation, while easing monetary policy lowers interest rates and may increase inflation. It is important for central banks to carefully consider these effects when making policy decisions to ensure economic stability.