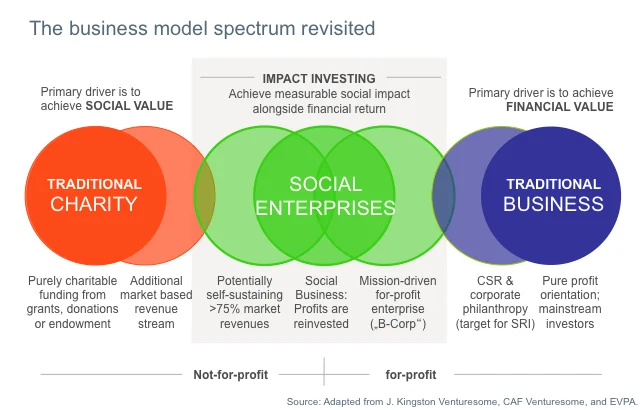
Social Entrepreneurship: Profit-Driven Business Models With Social Benefits is a concept that combines the principles of traditional entrepreneurship with a focus on creating positive social impact. This approach emphasizes the importance of generating financial profits while also addressing social or environmental issues. It involves the creation of innovative business models that prioritize social benefits alongside financial gains, aiming to create a more sustainable and equitable society.
In the realm of Social Entrepreneurship: Profit-Driven Business Models With Social Benefits, there is a growing interest in impact investing, which involves directing capital towards businesses that have the potential to generate positive social or environmental impact alongside financial returns. This approach goes beyond traditional corporate social responsibility, as it integrates social and environmental considerations into the core of a business’s operations and investment strategies. Social entrepreneurship also encompasses the concept of “shared value,” where companies create economic value in a way that also creates value for society by addressing its needs and challenges. This approach has gained traction as an effective way to drive business growth while simultaneously addressing social issues.
Social Entrepreneurship: Definition and Purpose
Social entrepreneurship refers to the use of business techniques to develop, fund, and implement solutions to social, cultural, or environmental issues. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs who measure their success in profit and return on investment, social entrepreneurs also prioritize the positive impact they have on society. Their main goal is to create sustainable and scalable change that addresses pressing social needs.
These entrepreneurs are driven by a desire to make a difference and create a better world. They often operate in areas where traditional markets have failed to address social problems, and they leverage their business acumen to create innovative, sustainable, and scalable solutions that benefit communities and society as a whole.
Key Characteristics of Profit-Driven Social Entrepreneurship
Profit-driven social entrepreneurship is characterized by its focus on generating financial returns while also creating positive social or environmental impact. These businesses are typically structured as for-profit entities and aim to achieve financial sustainability while addressing social issues. They prioritize the “double bottom line,” measuring success in terms of both financial profitability and social impact.
These enterprises often adopt innovative business models and strategies to achieve their dual objectives. They may engage in ethical sourcing, environmentally sustainable practices, or inclusive hiring to create social value while also differentiating themselves in the market. Additionally, they may prioritize transparency and accountability in their operations to build trust with consumers and stakeholders.
Examples of Profit-Driven Social Enterprises
There are numerous examples of profit-driven social enterprises across various industries. One notable example is TOMS, a company that operates on a “one-for-one” model, where for every pair of shoes purchased, a new pair is donated to a child in need. Another example is Warby Parker, an eyewear company that follows a similar model, providing a pair of glasses to someone in need for every pair sold.
Additionally, there are companies like Patagonia, which prioritizes environmental sustainability and ethical sourcing in its operations, and Greyston Bakery, a social enterprise that provides employment opportunities to individuals facing barriers to work, such as the formerly incarcerated. These businesses demonstrate how profit-driven models can be used to drive social impact in diverse ways.
Challenges and Opportunities in Profit-Driven Social Entrepreneurship
Profit-driven social entrepreneurship faces several challenges, including balancing financial sustainability with social impact, navigating regulatory requirements, and accessing funding for social initiatives. Additionally, measuring and quantifying social impact can be complex, requiring robust metrics and evaluation frameworks.
However, there are also significant opportunities in this space. With the growing demand for ethical and sustainable products and services, profit-driven social enterprises can tap into a market of socially conscious consumers. Moreover, partnerships with impact investors, philanthropic organizations, and government agencies can provide access to capital and resources to support their social missions.
Measuring Social Impact in Profit-Driven Social Enterprises
Measuring social impact is a critical aspect of profit-driven social entrepreneurship. It involves assessing the tangible and intangible effects of a business’s activities on the community, environment, or specific social issue it aims to address. This may include tracking metrics such as the number of beneficiaries reached, changes in behavior or attitudes, environmental outcomes, or improvements in quality of life.
Impact measurement allows social enterprises to demonstrate accountability, track progress toward their social goals, and make data-informed decisions to optimize their impact. It also provides transparency to stakeholders, including investors, customers, and the community, and helps build credibility and trust in the organization’s social mission.
Scaling Social Impact Through Profit-Driven Models
Scaling social impact is a central goal for profit-driven social enterprises. By achieving scalability, these businesses can expand their reach and deepen their influence on social issues. This may involve replicating successful business models in new locations, forming strategic partnerships, or leveraging technology to reach a larger audience.
Furthermore, scaling social impact often requires a focus on operational efficiency, innovation, and adaptability. Social enterprises may need to continually refine their strategies, streamline processes, and embrace new technologies to maximize their effectiveness and broaden their impact on society.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations for Profit-Driven Social Enterprises
Profit-driven social enterprises must navigate a complex landscape of regulatory and legal considerations. Depending on their business model and social mission, they may need to comply with specific industry regulations, tax requirements, and reporting standards. Additionally, they may need to consider the implications of different legal structures, such as benefit corporation status or certification as a B Corporation.
Understanding and adhering to these regulations is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and legitimacy as a social enterprise. It can also impact the organization’s access to funding, partnerships, and market opportunities, making it crucial for social entrepreneurs to seek legal counsel and stay informed about relevant laws and policies.
Building Sustainable Business Models for Social Impact
Building sustainable business models is a key consideration for profit-driven social enterprises. These models aim to create long-term value for both the business and society, ensuring that social impact initiatives are integrated into the core of the organization’s operations. This may involve developing innovative revenue streams, optimizing cost structures, and fostering a culture of social responsibility within the company.
Furthermore, sustainable business models require a focus on resilience and adaptability. Social enterprises must be able to weather economic challenges, market fluctuations, and other external factors while continuing to fulfill their social mission. This may involve diversifying income sources, building strong partnerships, and maintaining a strong commitment to their social objectives.
Investment and Funding Opportunities for Profit-Driven Social Enterprises
Investment and funding opportunities play a crucial role in supporting the growth and impact of profit-driven social enterprises. Impact investors, including venture capitalists, private equity firms, and foundations, are increasingly interested in supporting businesses that generate both financial returns and positive social outcomes. These investors provide capital, expertise, and networks to help social enterprises scale their operations and maximize their impact.
Additionally, social entrepreneurs can explore alternative funding sources, such as social impact bonds, crowdfunding, and grants from government agencies and philanthropic organizations. These funding mechanisms can provide the resources needed to develop and implement innovative solutions to complex social challenges, driving positive change in communities around the world.
| Definition | Social entrepreneurship refers to the use of business strategies to address social and environmental issues, providing innovative solutions that benefit society while also generating profits. |
|---|---|
| Business Model | Social enterprises typically have a dual mission of achieving financial sustainability and creating positive social impact. They may reinvest profits into furthering their social mission. |
| Examples | Examples of social enterprises include TOMS Shoes, which donates a pair of shoes for each one sold, and Grameen Bank, which provides microloans to alleviate poverty. |
| Impact | Social entrepreneurship aims to address societal problems in a sustainable way, often leading to long-term, systemic change and empowerment of communities. |