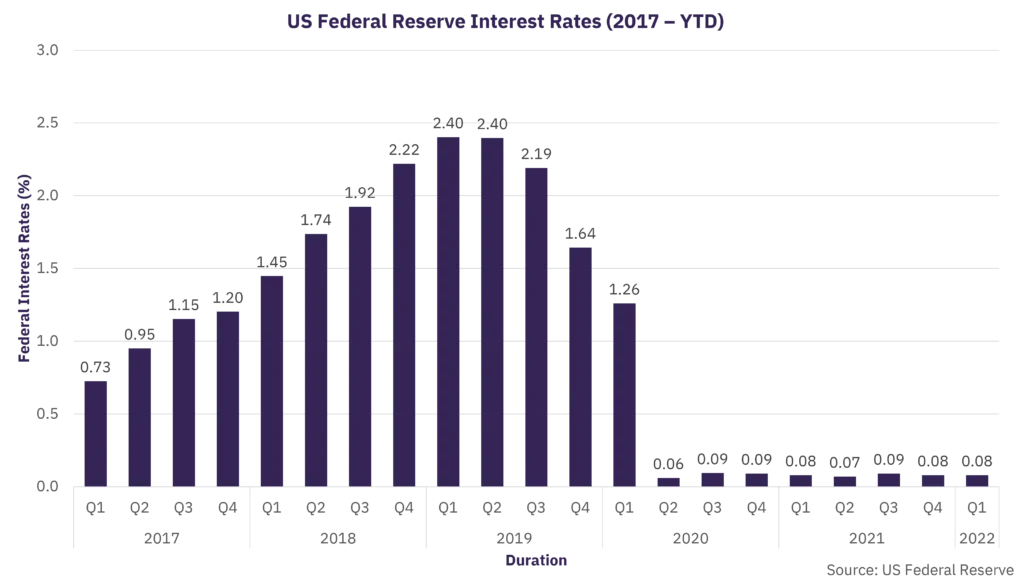
The Federal Reserve has announced an interest rate hike in an effort to curb inflation. This decision comes as a response to the rising inflation rates, which have been a cause for concern in the economy. The Federal Reserve aims to slow down the economy and reduce consumer spending by increasing interest rates, which will make borrowing more expensive. This move is expected to help stabilize prices and prevent the economy from overheating.
Many people are curious about the impact of the interest rate hike on mortgage rates and loan payments. Homebuyers and existing homeowners are eager to understand how this decision will affect their ability to afford and qualify for loans. Additionally, investors are closely watching the stock market’s reaction to the news, as higher interest rates can influence company valuations and investment strategies. It is also important to consider how the interest rate hike will affect the cost of borrowing for businesses and its potential impact on economic growth.
The Federal Reserve’s Decision
The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, has announced an interest rate hike in an effort to curb inflation. This decision comes as a response to the rising prices across various sectors of the economy, including housing, energy, and food.
The Federal Reserve aims to use the interest rate hike as a tool to slow down spending and borrowing, which in turn can help to reduce inflationary pressures. By increasing the cost of borrowing, the central bank hopes to moderate the demand for goods and services, ultimately easing the upward pressure on prices.
Impact on Borrowing Costs
One immediate impact of the interest rate hike will be an increase in borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. This means that individuals and companies will face higher interest rates on loans for mortgages, car purchases, and business investments. As a result, the cost of borrowing money will rise, potentially leading to reduced spending and investment.
Higher borrowing costs can also affect the housing market, as mortgage rates are likely to increase. This could result in a slowdown in home purchases and a decrease in demand for new mortgages, impacting the overall real estate industry.
Stock Market Reaction
The announcement of an interest rate hike by the Federal Reserve can have a significant impact on the stock market. Historically, stock prices have tended to fall in response to interest rate hikes, as higher borrowing costs can reduce corporate profitability and consumer spending.
Investors may also reevaluate their investment portfolios in response to the interest rate hike, potentially shifting their assets away from stocks and towards other investment options. This can lead to increased volatility in the stock market as investors react to the changing economic landscape.
Response from Businesses and Consumers
Businesses and consumers are likely to adjust their behavior in response to the interest rate hike. For businesses, higher borrowing costs may lead to reduced investment in new projects and expansion plans. This could potentially result in slower economic growth and job creation in the short term.
Consumers may also feel the impact of the interest rate hike, as higher borrowing costs can lead to reduced spending on big-ticket items such as cars and homes. Additionally, higher interest rates on credit cards and other forms of consumer debt may lead to increased financial strain for some households.
International Implications
The Federal Reserve’s decision to raise interest rates can have implications beyond the borders of the United States. Higher interest rates in the U.S. may lead to a stronger U.S. dollar, which can impact international trade and the competitiveness of U.S. exports.
Furthermore, emerging markets and developing economies may face challenges as a result of the interest rate hike, as higher U.S. interest rates can lead to capital outflows from these countries and put pressure on their currencies and financial markets.
Long-Term Inflation Outlook
While the interest rate hike is aimed at curbing short-term inflationary pressures, its impact on the long-term inflation outlook remains to be seen. The Federal Reserve will continue to monitor economic indicators and inflation data to assess whether further action is needed to maintain price stability in the long run.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of interest rate hikes in controlling inflation may vary depending on the underlying causes of inflation and the overall state of the economy. The Federal Reserve’s decisions will continue to be guided by its dual mandate of maximum employment and stable prices.
Communication from the Federal Reserve
In addition to the interest rate hike itself, the Federal Reserve’s communication regarding its decision can also influence market expectations and behavior. The central bank’s public statements and press conferences play a crucial role in shaping perceptions about the future direction of monetary policy and the economy.
Clear and transparent communication from the Federal Reserve can help to provide guidance to businesses, investors, and the general public about the central bank’s policy intentions and the factors driving its decision-making process. This can contribute to greater stability and predictability in financial markets.
Future Policy Considerations
Looking ahead, the Federal Reserve will continue to assess economic data and trends to determine its future policy actions. The central bank will need to weigh the potential impact of interest rate hikes on economic growth, employment, and inflation, while also considering external factors such as geopolitical events and global economic conditions.
Future policy considerations may also include the pace and magnitude of interest rate adjustments, as well as the potential use of other monetary policy tools to achieve the Federal Reserve’s objectives of price stability and maximum sustainable employment.
| Date | Interest Rate | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| March 16, 2022 | 0.25% | To curb inflation |
Federal Reserve announced a 0.25% interest rate hike on March 16, 2022, in an effort to curb inflation. This decision reflects the central bank’s proactive approach to managing the economy and keeping inflation in check.