Global Surge in Dengue Fever: How Climate Change Is Worsening the Crisis is a pressing issue that is gaining attention worldwide. Dengue fever, a mosquito-borne viral infection, has seen a significant increase in cases in recent years, with climate change being identified as a major contributing factor. The rise in global temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns have created more favorable conditions for the Aedes aegypti mosquito, which transmits the dengue virus, to thrive and spread. As a result, the incidence of dengue fever has been on the rise, posing a serious public health threat in many regions.
This concerning trend has sparked growing interest and concern among researchers, policymakers, and the general public alike. With the link between climate change and the surge in dengue fever becoming increasingly evident, there is a heightened focus on understanding the specific ways in which environmental factors are exacerbating the crisis. Additionally, there is a growing demand for innovative strategies and interventions to mitigate the impact of climate change on the spread of dengue fever. As the global community grapples with these challenges, it is imperative to explore the intersection of climate change and public health in order to develop effective and sustainable solutions.
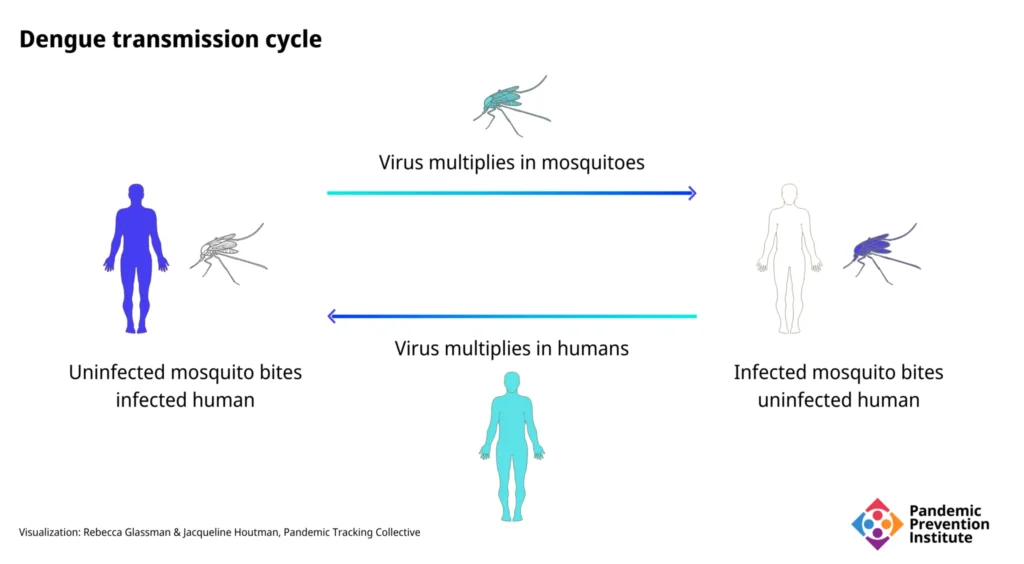
1. Understanding Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne viral infection that causes flu-like symptoms and can develop into a potentially lethal complication known as severe dengue. The virus is transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female Aedes mosquitoes, primarily Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Symptoms of dengue fever include high fever, severe headache, pain behind the eyes, joint and muscle pain, rash, and mild bleeding, such as nose or gum bleeding.
While dengue fever is found in many tropical and subtropical regions, the incidence of the disease has increased dramatically in recent decades. Factors such as urbanization, population growth, and increased international travel have contributed to the spread of dengue fever. Additionally, climate change has played a significant role in exacerbating the global surge in dengue fever.
2. The Link Between Climate Change and Dengue Fever
Climate change has created more favorable conditions for the breeding and spread of Aedes mosquitoes, the vectors responsible for transmitting the dengue virus. Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns have led to an expansion of the geographical range of these mosquitoes, exposing more people to the risk of dengue fever. Additionally, extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and heavy rainfall, create breeding grounds for mosquitoes by leaving behind stagnant water, which is essential for their reproduction.
Moreover, warmer temperatures can accelerate the replication of the dengue virus within mosquitoes, reducing the incubation period of the virus and increasing the likelihood of transmission to humans. These environmental changes have contributed to the increasing incidence of dengue fever in regions that were previously unaffected by the disease.
3. Impact on Public Health
The global surge in dengue fever has significant implications for public health systems and communities. The disease places a considerable burden on healthcare facilities, especially in regions with limited resources. The increase in dengue cases strains medical services and can overwhelm hospitals, leading to challenges in providing adequate care for patients.
Furthermore, the economic impact of dengue fever is substantial, as it results in productivity losses due to illness and healthcare expenditures. Families also bear the financial burden of caring for affected individuals, particularly in cases of severe dengue that require hospitalization and intensive treatment. The societal and economic consequences of dengue fever underscore the importance of addressing the underlying factors, including climate change, that contribute to its prevalence.
4. Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
To address the exacerbation of dengue fever by climate change, adaptation and mitigation strategies are essential. These strategies involve comprehensive mosquito control measures, including the elimination of breeding sites, use of insecticides, and community engagement to raise awareness about preventive actions. Additionally, urban planning and design can play a role in reducing mosquito habitats and minimizing exposure to mosquitoes, ultimately curbing the spread of dengue fever.
Furthermore, strengthening public health surveillance and response systems is crucial for early detection and management of dengue outbreaks. Improved healthcare infrastructure and capacity building for healthcare professionals are also integral to effectively manage the increasing burden of dengue fever. Addressing climate change through mitigation efforts, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, is a long-term approach to mitigating the impact of environmental factors on the prevalence of dengue fever.
5. Research and Innovation
Ongoing research and innovation are fundamental to understanding the complex interactions between climate change and the spread of dengue fever. This includes studying the ecological dynamics of Aedes mosquitoes, the genetic diversity of the dengue virus, and the influence of environmental factors on vector behavior and virus transmission. Advances in technology and data analysis also contribute to the development of predictive models for dengue outbreaks, enabling proactive measures to be implemented.
Furthermore, the development of vaccines and novel vector control methods remains a priority in the fight against dengue fever. Research efforts aim to enhance vaccine efficacy, expand access to immunization, and explore alternative approaches to mosquito control, such as genetic modification and biological control agents.
6. Community Engagement and Education
Community engagement and education are essential components of dengue fever prevention and control efforts. Empowering communities with knowledge about the transmission of dengue, the importance of eliminating mosquito breeding sites, and recognizing symptoms of the disease can lead to proactive measures at the grassroots level. Educational campaigns, outreach programs, and partnerships with local organizations contribute to raising awareness and promoting behavioral changes that reduce the risk of dengue fever.
Furthermore, collaboration with schools, community leaders, and healthcare providers facilitates the dissemination of information and encourages community participation in vector control activities. Engaging individuals and communities in dengue prevention fosters a sense of ownership and collective responsibility in combating the disease.
7. International Cooperation and Policy Action
Given the global nature of dengue fever and its association with climate change, international cooperation and policy action are imperative. Collaborative efforts among countries, international organizations, and research institutions facilitate the exchange of knowledge, best practices, and resources to address the challenges posed by dengue fever. This includes sharing epidemiological data, coordinating research initiatives, and supporting capacity-building programs in endemic regions.
At the policy level, prioritizing investments in public health infrastructure, vector control programs, and climate adaptation measures is essential for mitigating the impact of dengue fever. Integrating dengue prevention and control into broader climate change adaptation strategies and health policies strengthens resilience to the growing threat of vector-borne diseases influenced by environmental changes.
8. The Way Forward: Addressing Climate Change and Dengue Fever
Addressing the intersection of climate change and the global surge in dengue fever requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses environmental, public health, and socio-economic dimensions. This entails integrating climate resilience into healthcare systems, fostering sustainable urban development, and promoting policies that mitigate the drivers of climate change. Additionally, investing in research, innovation, and community engagement is essential for developing effective solutions to prevent and control dengue fever in a changing climate.
Ultimately, proactive measures to address climate change, coupled with comprehensive dengue prevention and control strategies, are critical for reducing the burden of dengue fever and safeguarding public health worldwide. By recognizing the interconnectedness of environmental and human health, societies can work towards building resilient and sustainable communities that are better equipped to confront the challenges posed by a changing climate and the spread of vector-borne diseases.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Issue | Global surge in Dengue Fever |
| Cause | Climate Change |
| Impact | Worsening the crisis |