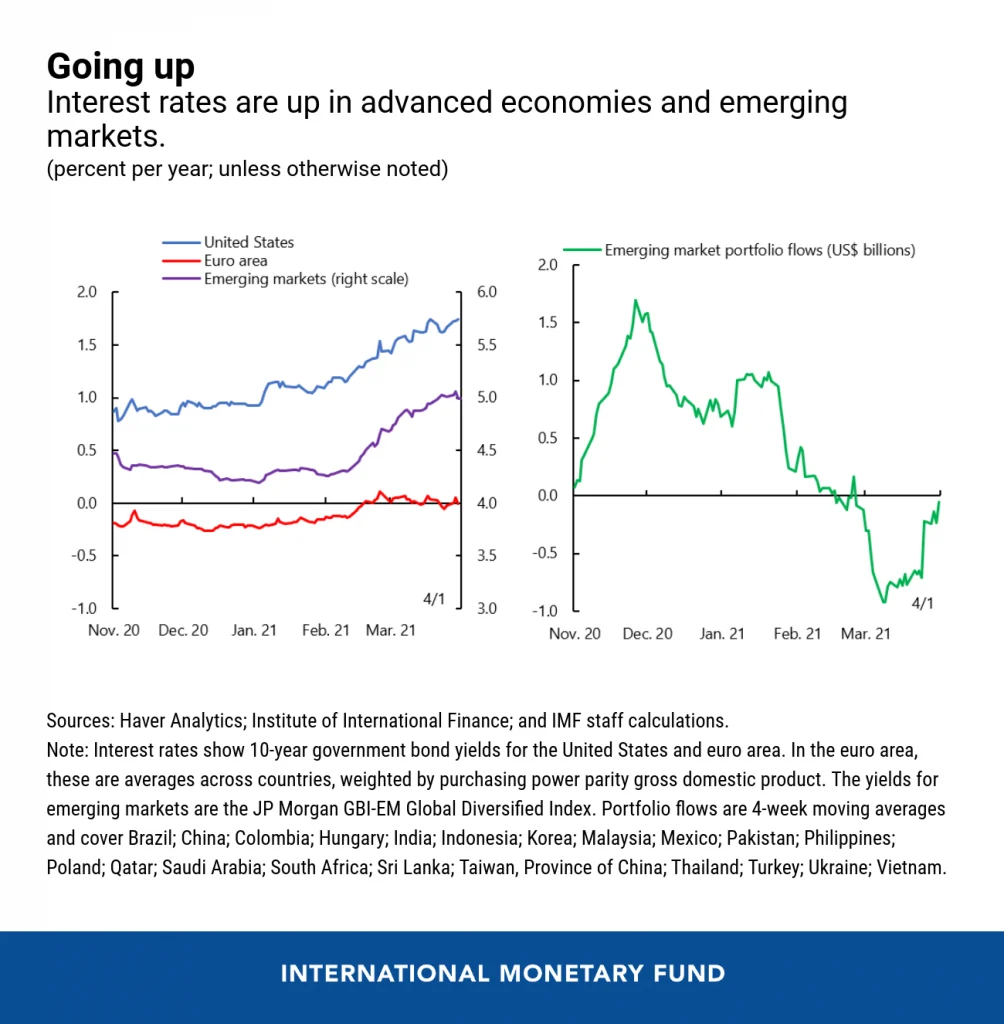
Global Economic Outlook: How Rising Interest Rates Are Affecting Emerging Markets is a topic of great concern in today’s financial world. As central banks around the world begin to raise interest rates in response to inflationary pressures, emerging markets are facing a variety of challenges. These challenges include currency depreciation, capital outflows, and increased borrowing costs, all of which can have significant impacts on economic growth and stability in these countries.
The impact of rising interest rates on emerging markets is a matter of great interest and concern for investors and policymakers alike. As higher interest rates make it more expensive for emerging market governments and companies to borrow money, there is a risk of decreased investment and economic activity in these countries. Additionally, the potential for currency depreciation and capital outflows can further exacerbate the challenges faced by these economies. Understanding how these factors interact and influence each other is crucial for anticipating the future outlook for emerging markets in the face of rising interest rates.
Impact of Rising Interest Rates on Emerging Markets
As global interest rates rise, emerging markets are facing significant challenges in managing their economic stability. The higher cost of borrowing reduces consumer and business spending, leading to a slowdown in economic growth. Emerging markets with high levels of external debt are particularly vulnerable to the impact of rising interest rates, as the cost of servicing their debt increases, putting pressure on their currencies and leading to potential financial instability.
Furthermore, rising interest rates in developed countries attract investors away from emerging markets in search of higher returns, leading to capital outflows and currency depreciation. This can further exacerbate inflationary pressures and increase the cost of imports, leading to a deterioration in the current account balance of emerging market economies.
Challenges Faced by Emerging Market Central Banks
Central banks in emerging markets are tasked with the difficult job of managing the impact of rising interest rates on their economies. They often face a trade-off between controlling inflation and supporting economic growth. In response to rising global interest rates, many emerging market central banks have had to tighten monetary policy, raising their own interest rates to maintain exchange rate stability and control inflation.
However, higher interest rates can also dampen domestic investment and consumption, potentially leading to a slowdown in economic activity. This poses a dilemma for central banks in emerging markets, as they strive to strike a balance between managing inflationary pressures and supporting sustainable economic growth in the face of external headwinds.
Currency Depreciation and Inflationary Pressures
Rising interest rates in developed countries can lead to currency depreciation in emerging markets, as investors flock to higher-yielding assets in search of better returns. A weaker domestic currency can fuel inflationary pressures by increasing the cost of imported goods and raw materials, leading to higher consumer prices and reduced purchasing power.
Furthermore, currency depreciation can also increase the cost of servicing foreign currency-denominated debt, putting additional strain on the financial stability of emerging market economies. Central banks may intervene in the foreign exchange market to stabilize their currencies, but this can deplete foreign exchange reserves and limit their ability to respond to future economic shocks.
Impact on External Debt and Fiscal Sustainability
Many emerging markets rely on external borrowing to finance their development and infrastructure projects. The rise in global interest rates increases the cost of servicing external debt, putting pressure on the fiscal sustainability of these economies. Governments may have to allocate a larger portion of their budget to debt servicing, which can limit their ability to invest in social welfare programs and essential public services.
Furthermore, the increased cost of borrowing may make it more challenging for emerging market governments and corporates to access international capital markets, potentially leading to a slowdown in investment and economic growth. This can create a vicious cycle where higher interest rates lead to lower growth, further straining the fiscal position of emerging market economies.
Investment and Capital Flows in Emerging Markets
Rising interest rates in developed countries can lead to a shift in investment and capital flows away from emerging markets. Investors may seek higher returns in developed markets, leading to capital outflows from emerging markets and putting downward pressure on their currencies. This can reduce the availability of investment capital for emerging market businesses and governments, potentially leading to a slowdown in economic activity.
Furthermore, the prospect of higher returns in developed markets may lead to a reduction in foreign direct investment in emerging markets, as investors reallocate their capital to take advantage of rising interest rates. This can have long-term implications for the growth and development of emerging market economies, as they may face challenges in attracting the necessary investment for infrastructure and industrial development.
Policy Responses and Mitigation Strategies
Emerging market governments and central banks have implemented various policy responses to mitigate the impact of rising interest rates. These may include tightening monetary policy to control inflation, implementing fiscal reforms to improve debt sustainability, and diversifying sources of financing to reduce reliance on external borrowing.
Additionally, some emerging market economies have sought to attract and retain foreign investment by implementing structural reforms to improve the business environment and enhance investor confidence. These reforms may include measures to streamline regulations, improve governance, and enhance transparency, making emerging markets more attractive destinations for investment despite the challenges posed by rising interest rates.
Long-Term Implications for Economic Development
The impact of rising interest rates on emerging markets has long-term implications for their economic development. It can lead to a slowdown in investment, reduced access to international capital, and challenges in managing external debt, potentially hindering the long-term growth prospects of these economies. Furthermore, the need to balance inflation control with supporting economic growth poses significant challenges for policymakers in emerging markets.
However, the experience of managing the impact of rising interest rates can also serve as an opportunity for emerging markets to strengthen their economic resilience and implement structural reforms that enhance their competitiveness and attractiveness to investors. By addressing underlying vulnerabilities and enhancing their policy frameworks, emerging markets can position themselves for sustainable and inclusive economic development in the face of global interest rate dynamics.
| Country | Impact of Rising Interest Rates |
|---|---|
| Turkey | Increased borrowing costs for businesses and consumers |
| Brazil | Depreciation of the currency and capital outflows |
| India | Pressure on inflation and current account deficits |
| South Africa | Reduced investor confidence and slower economic growth |
The rising interest rates are having significant impacts on emerging markets. Countries like Turkey are experiencing increased borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Brazil is facing the depreciation of its currency and capital outflows. In India, there is pressure on inflation and current account deficits, while South Africa is seeing reduced investor confidence and slower economic growth. Overall, emerging markets are facing various challenges as a result of the rising interest rates.