The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in surveillance and privacy has sparked ethical concerns in the tech industry. As AI technology continues to advance, questions about its role in monitoring and data collection have become increasingly important. Many people are debating the potential impact of AI on privacy rights and the ethical implications of using AI for surveillance purposes. There is a growing need for a thoughtful and transparent discussion about the ethical considerations surrounding AI’s role in surveillance and privacy. This debate highlights the complex intersection of technology, ethics, and individual rights.
The discussion around AI’s involvement in surveillance and privacy also raises questions about data protection, civil liberties, and government oversight. People are curious about the potential consequences of widespread AI surveillance on personal freedoms and democratic societies. Additionally, there is a growing interest in exploring alternative methods of protecting privacy while still leveraging AI for security purposes. The debate over AI’s role in surveillance and privacy extends beyond the technological realm, touching on broader societal and ethical implications.
1. The Rise of AI in Surveillance
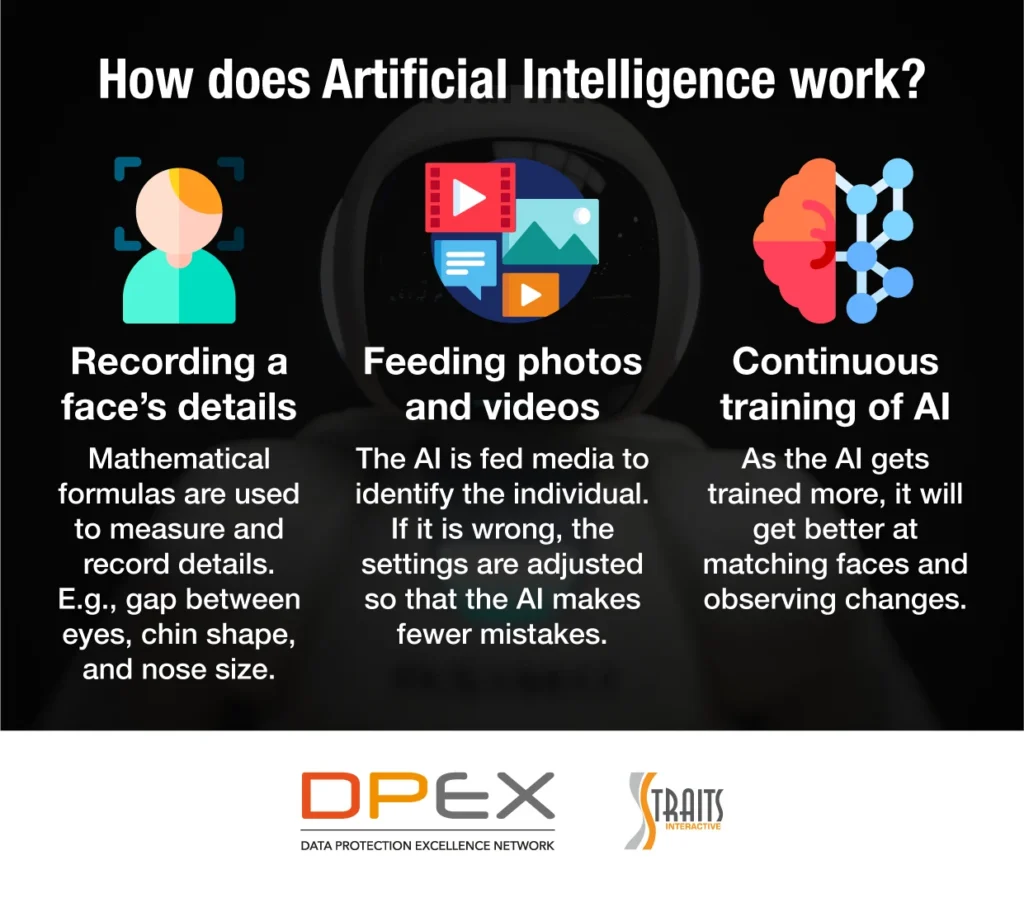
Advancements in artificial intelligence have led to the widespread use of AI in surveillance systems. These systems are capable of analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time, enabling the monitoring of public spaces, tracking individuals, and identifying potential security threats. AI-based surveillance technologies have been adopted by governments, law enforcement agencies, and private companies, raising concerns about the impact on privacy and civil liberties.
While proponents argue that AI-powered surveillance enhances public safety and security, critics warn about the potential for abuse and misuse. The deployment of facial recognition technology, predictive policing algorithms, and social media monitoring tools has sparked debates about the ethical implications of AI surveillance and the need for robust regulations to safeguard individual rights.
2. Privacy Risks and Data Protection
The use of AI in surveillance raises significant privacy risks and data protection concerns. As surveillance systems collect and analyze personal information, such as biometric data, location tracking, and online activities, there is a heightened risk of privacy infringements and unauthorized access to sensitive data. The lack of transparency and accountability in AI surveillance practices further exacerbates these risks, as individuals may not be aware of the extent to which their privacy is being compromised.
Moreover, the potential for data breaches and cyber attacks on AI-powered surveillance systems poses a threat to data security. The aggregation of massive datasets and the potential for algorithmic biases also raise questions about the fairness and accuracy of surveillance activities. As such, there is a pressing need to establish clear guidelines for the ethical use of AI in surveillance, including robust data protection measures and mechanisms for obtaining informed consent from individuals who are subjected to surveillance.
3. Ethical Implications of Biometric Surveillance
The widespread adoption of biometric surveillance technologies, powered by AI, has sparked ethical concerns regarding the collection and use of biometric data. Facial recognition systems, iris scanning technology, and gait analysis algorithms are capable of uniquely identifying individuals, raising questions about the potential for mass surveillance and the erosion of anonymity in public spaces. The ethical implications of biometric surveillance extend to issues of consent, accuracy, and the potential for discriminatory practices.
Concerns have been raised about the misuse of biometric data for tracking and monitoring individuals without their knowledge or consent, as well as the potential for misidentification and false positives. Additionally, the lack of standards for the ethical use of biometric surveillance poses challenges in ensuring that these technologies are deployed in a manner that respects individual privacy rights and mitigates the risk of surveillance abuse.
4. Algorithmic Bias and Discriminatory Practices
The use of AI in surveillance has raised alarms about the potential for algorithmic bias and discriminatory practices. Machine learning algorithms utilized in surveillance systems rely on training data that may reflect societal biases and prejudices, leading to the disproportionate targeting of certain demographic groups and the reinforcement of existing inequalities. This raises ethical concerns about the fairness and impartiality of AI-powered surveillance, particularly in the context of law enforcement and criminal justice.
Instances of algorithmic bias in facial recognition technology, predictive policing algorithms, and risk assessment tools have drawn attention to the need for thorough scrutiny of AI systems to identify and mitigate biases. The ethical imperative to address algorithmic bias in surveillance extends to the development of inclusive and diverse training datasets, as well as the implementation of oversight mechanisms to ensure that AI technologies do not perpetuate discriminatory outcomes.
5. Transparency and Accountability in AI Surveillance
The lack of transparency and accountability in AI surveillance poses significant ethical challenges. The opaque nature of surveillance algorithms and the secretive deployment of surveillance technologies hinder public oversight and scrutiny, undermining the principles of accountability and democratic governance. As AI systems increasingly automate surveillance processes, there is a growing need for transparency measures to ensure that the decision-making processes and outcomes of AI surveillance are subject to public scrutiny.
Furthermore, the lack of accountability mechanisms for addressing instances of surveillance overreach, privacy violations, or algorithmic errors raises concerns about the unchecked power of AI in surveillance. Ethical frameworks for AI surveillance must prioritize transparency, accountability, and mechanisms for redress to uphold the principles of fairness, justice, and individual rights in the face of expanding surveillance capabilities.
6. Safeguarding Civil Liberties and Individual Rights
The debate over AI’s role in surveillance revolves around the fundamental imperative of safeguarding civil liberties and individual rights. The expansion of AI-powered surveillance has prompted discussions about the balance between public safety and the protection of privacy, free expression, and freedom of assembly. Ethical considerations dictate the need to establish clear boundaries for the permissible use of AI in surveillance to prevent encroachments on civil liberties.
As AI surveillance capabilities continue to evolve, there is a growing need to ensure that legal and ethical safeguards are in place to prevent unwarranted intrusions into individuals’ private lives and activities. This necessitates robust privacy laws, judicial oversight, and public discourse to address the ethical tensions between security imperatives and the preservation of individual rights in an increasingly surveilled society.
7. International Perspectives on AI Surveillance Ethics
The ethical debate over AI’s role in surveillance extends to international perspectives, as different countries grapple with the implications of AI-powered surveillance within their respective legal and cultural contexts. Divergent approaches to privacy, data protection, and government surveillance practices shape the ethical frameworks governing AI surveillance across national boundaries. International collaboration and dialogue are essential to address the ethical challenges posed by the global diffusion of AI surveillance technologies.
Furthermore, disparities in governance and oversight mechanisms for AI surveillance raise questions about the harmonization of ethical standards and best practices on a global scale. The ethical considerations surrounding AI surveillance require cross-border cooperation to establish norms that uphold human rights, democratic values, and the ethical use of AI in surveillance to mitigate potential abuses and ensure accountability.
8. The Path Forward: Ethical Guidelines and Regulatory Frameworks
Addressing the ethical concerns surrounding AI’s role in surveillance necessitates the development of comprehensive guidelines and regulatory frameworks. Ethical guidelines should encompass principles of transparency, accountability, fairness, and the protection of individual rights in the deployment of AI surveillance technologies. Regulatory frameworks must align with ethical principles to establish clear boundaries for the collection, use, and retention of data in surveillance activities.
The involvement of multi-stakeholder engagement, including government entities, technology developers, civil society organizations, and privacy advocates, is crucial in shaping ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks for AI surveillance. By fostering collaboration and consensus-building, it is possible to establish ethical norms that uphold human dignity, privacy rights, and the responsible use of AI in surveillance to mitigate potential harms and safeguard democratic values.
| Ethical Concerns | Arguments |
|---|---|
| Privacy | AI technology can be used to invade individuals’ privacy through surveillance and data collection. |
| Surveillance | AI-powered surveillance systems raise concerns about mass monitoring, facial recognition, and tracking of individuals’ movements. |
| Autonomy | AI has the potential to infringe on individuals’ autonomy by making decisions that impact their lives without their consent. |
| Discrimination | There is a risk of AI systems perpetuating and amplifying existing biases, leading to discrimination against certain groups. |