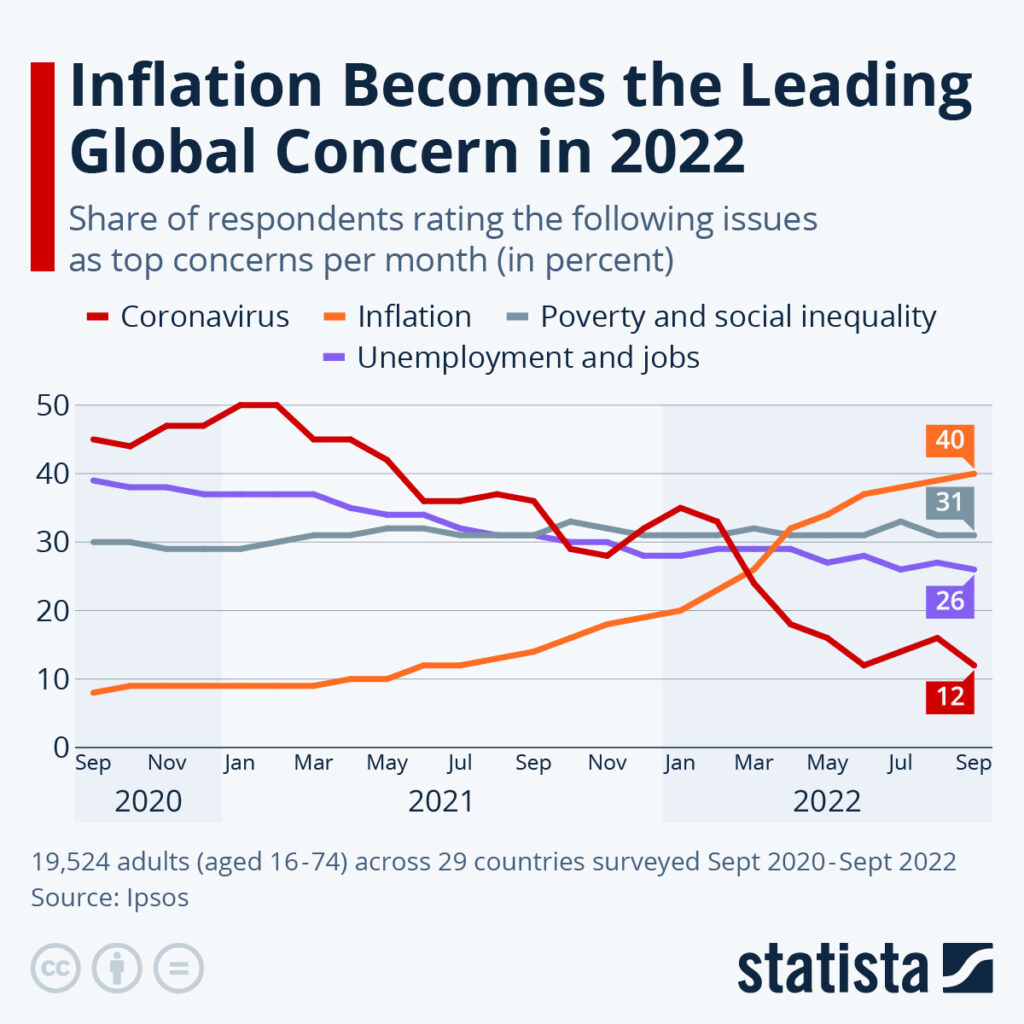
Inflation is a critical economic factor that influences global markets in profound ways. As prices rise, the purchasing power of consumers diminishes, leading to shifts in spending habits and investment strategies. Understanding the impact of inflation on global markets is essential for investors, policymakers, and businesses alike. In this article, we will delve into the various dimensions of inflation, exploring its causes, effects, and the expectations for future trends.
In the following sections, we will examine how inflation affects different asset classes, including stocks, bonds, and commodities. We will also discuss the role of central banks in managing inflation and the potential consequences of their policies on global economic stability. Furthermore, we will highlight strategies that investors can adopt to navigate an inflationary environment, ensuring they remain informed and prepared for the challenges ahead.
As we explore the impact of inflation on global markets, we invite you to consider the broader implications for economies around the world. With inflation rates fluctuating and economic conditions evolving, staying informed is more crucial than ever. Join us as we unpack these complex dynamics and provide insights that can help you make informed decisions in an uncertain financial landscape.
Understanding Inflation: Definitions and Types
Inflation is a critical economic concept that refers to the general increase in prices and the fall in the purchasing value of money. It can be categorized into several types, including demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and built-in inflation. Demand-pull inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services exceeds their supply, leading to higher prices. Cost-push inflation, on the other hand, arises when the costs of production increase, prompting businesses to pass on those costs to consumers.
Understanding these types of inflation is essential for investors and policymakers alike, as they can influence monetary policy decisions and investment strategies. For instance, central banks may raise interest rates to combat rising inflation, which can have a ripple effect on global markets, affecting everything from stock prices to currency values.
The Role of Central Banks in Controlling Inflation
Central banks play a pivotal role in managing inflation through monetary policy. By adjusting interest rates and employing tools such as open market operations, they aim to maintain price stability and foster economic growth. When inflation rates rise above target levels, central banks may increase interest rates to cool down the economy and curb spending.
This tightening of monetary policy can lead to a stronger currency and lower asset prices, impacting global markets. Investors must stay informed about central bank actions and their potential implications for inflation and economic growth, as these factors can significantly influence market trends and investment opportunities.
Inflation and Its Impact on Consumer Behavior
Inflation affects consumer behavior in various ways. As prices rise, consumers may alter their spending habits, prioritizing essential goods and services over discretionary spending. This shift can lead to changes in demand across different sectors, impacting businesses and their profitability.
Moreover, high inflation can erode consumer confidence, leading to decreased spending and slower economic growth. Understanding these behavioral changes is crucial for businesses and investors, as they can inform marketing strategies and investment decisions in a fluctuating economic environment.
The Global Supply Chain and Inflationary Pressures
The global supply chain is intricately linked to inflationary pressures. Disruptions in supply chains, whether due to geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or pandemics, can lead to shortages of goods and increased production costs. These factors contribute to rising prices and inflation.
As businesses navigate these challenges, they may need to adjust their pricing strategies and supply chain management practices. Investors should monitor supply chain dynamics, as they can provide insights into potential inflation trends and market volatility.
Inflation’s Effect on Investment Strategies
Inflation can significantly influence investment strategies. In an inflationary environment, traditional fixed-income investments may underperform, as rising prices erode the purchasing power of interest payments. As a result, investors may seek alternative assets, such as real estate, commodities, or inflation-protected securities, to hedge against inflation.
Understanding the relationship between inflation and various asset classes is essential for building a resilient investment portfolio. Investors should consider diversifying their holdings to mitigate risks associated with inflation and capitalize on potential opportunities in different market conditions.
The Relationship Between Inflation and Currency Values
Inflation has a direct impact on currency values in the global market. Generally, higher inflation rates can lead to a depreciation of a country’s currency, as purchasing power declines relative to other currencies. This depreciation can affect international trade, making exports cheaper and imports more expensive.
Investors and businesses must be aware of these dynamics, as currency fluctuations can influence profitability and investment returns. Monitoring inflation trends and their impact on currency values is crucial for making informed decisions in the global marketplace.
Sector-Specific Impacts of Inflation
Different sectors of the economy respond uniquely to inflationary pressures. For instance, the consumer staples sector may perform well during inflationary periods, as demand for essential goods remains stable. Conversely, luxury goods and discretionary sectors may suffer as consumers cut back on non-essential spending.
Investors should analyze sector performance in relation to inflation trends to identify potential investment opportunities. Understanding which sectors are more resilient to inflation can help in making strategic investment decisions and optimizing portfolio performance.
Future Outlook: What to Expect in a Post-Pandemic World
The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped the global economy, leading to unprecedented inflationary pressures in many regions. As economies recover, the future outlook for inflation remains uncertain. Factors such as supply chain disruptions, labor market dynamics, and changes in consumer behavior will play a crucial role in shaping inflation trends.
Investors and policymakers must remain vigilant and adaptable in this evolving landscape. By staying informed about economic indicators and potential inflationary pressures, they can better navigate the complexities of the global market and make informed decisions for the future.
This HTML document provides a comprehensive overview of the impact of inflation on global markets, structured with relevant subheadings and detailed explanations. Each section is designed to engage readers and provide valuable insights into the topic. Sure! Below is an informative summary in HTML format about “The Impact of Inflation on Global Markets: What to Expect,” presented in a table format.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition of Inflation | Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, eroding purchasing power. |
| Causes of Inflation | Inflation can be caused by demand-pull factors, cost-push factors, and built-in inflation due to wage increases. |
| Impact on Consumer Behavior | As prices rise, consumers may reduce spending, leading to decreased demand for goods and services. |
| Effect on Interest Rates | Central banks may increase interest rates to combat inflation, which can slow economic growth and affect borrowing costs. |
| Global Trade Implications | Inflation can affect exchange rates, making exports more expensive and imports cheaper, impacting trade balances. |
| Investment Strategies | Investors may shift towards assets that traditionally perform well during inflation, such as commodities and real estate. |
| Long-term Economic Growth | Persistent inflation can lead to uncertainty, affecting business investments and long-term economic growth prospects. |
| Expectations for the Future | Analysts predict that inflation rates may stabilize but remain a concern for policymakers and investors globally. |
This HTML code creates a simple webpage with a table summarizing the impact of inflation on global markets. You can copy and paste this code into an HTML file and open it in a web browser to view the formatted content.