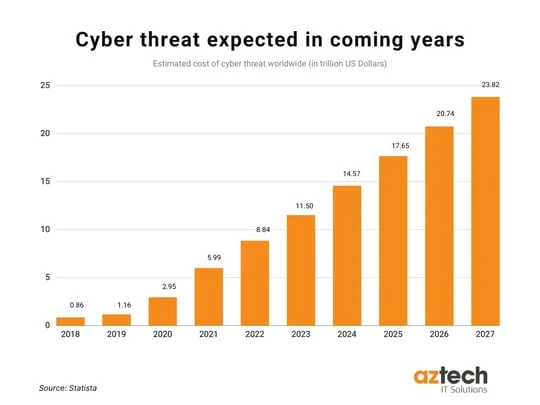
Cybersecurity in 2024: Top Trends and Emerging Threats to Watch is a critical topic in today’s digital world. As technology continues to advance, the landscape of cybersecurity is constantly evolving, and it’s important to stay informed about the latest trends and emerging threats. From artificial intelligence and machine learning to quantum computing and IoT devices, the cybersecurity industry is facing new challenges and opportunities in 2024. Understanding these trends and threats is essential for individuals and organizations to protect their digital assets and sensitive information.
As we look ahead to Cybersecurity in 2024: Top Trends and Emerging Threats to Watch, it’s important to consider the impact of blockchain technology, ransomware attacks, and data privacy regulations. The rise of decentralized finance and cryptocurrency has introduced new cybersecurity risks, while ransomware attacks continue to target businesses and individuals. Additionally, evolving data privacy regulations are shaping the way organizations handle and protect personal information, creating both challenges and opportunities in the cybersecurity landscape. Staying ahead of these emerging threats and trends is crucial for maintaining a secure digital environment.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing the cybersecurity landscape, enabling organizations to detect and respond to threats more effectively than ever before. AI and ML technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential security breaches in real time. This allows for proactive threat detection and automated response, reducing the burden on human analysts and improving overall security posture.
Furthermore, AI and ML are being used to develop advanced security tools and solutions, such as predictive analytics, behavioral analysis, and adaptive authentication. These technologies are continuously evolving to stay ahead of sophisticated cyber threats, making AI and ML crucial components of modern cybersecurity strategies.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) Security Challenges
Internet of Things (IoT) Security Challenges
The proliferation of internet-connected devices in homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure has created new security challenges. IoT devices often have limited computing resources and are deployed in diverse and uncontrolled environments, making them attractive targets for cyber attacks. As a result, securing IoT devices and networks has become a top priority for organizations and manufacturers.
In 2024, we can expect to see a focus on IoT security standards and regulations, as well as the development of specialized security solutions for IoT environments. Additionally, efforts to secure the entire IoT ecosystem, from device hardware to communication protocols, will be crucial in mitigating the growing risks associated with interconnected devices.
3. Rise of Quantum Computing Threats
Rise of Quantum Computing Threats
While quantum computing holds great promise for solving complex problems, it also poses a significant threat to traditional encryption algorithms. In the coming years, the emergence of powerful quantum computers could render many existing cryptographic methods obsolete, potentially exposing sensitive data to malicious actors.
Cybersecurity experts are actively researching and developing quantum-resistant encryption techniques to prepare for this impending threat. Organizations will need to stay ahead of the curve by transitioning to quantum-safe cryptographic solutions and ensuring that their data remains secure in the era of quantum computing.
4. Evolving Ransomware Tactics and Defenses
Evolving Ransomware Tactics and Defenses
Ransomware attacks have become increasingly sophisticated and damaging, targeting organizations of all sizes across various industries. In 2024, we can anticipate the continued evolution of ransomware tactics, including the use of advanced encryption methods, double extortion schemes, and targeted attacks on critical infrastructure.
To combat these evolving threats, organizations will need to invest in robust backup and recovery strategies, implement multi-layered security controls, and prioritize employee training and awareness. Additionally, collaboration between law enforcement agencies, cybersecurity vendors, and industry partners will be essential in disrupting ransomware operations and holding threat actors accountable.
5. Cloud Security and Compliance Challenges
Cloud Security and Compliance Challenges
The widespread adoption of cloud computing has transformed the way organizations store, process, and manage data. However, this shift to the cloud has introduced complex security and compliance challenges, especially as regulations and standards continue to evolve.
In 2024, we can expect to see a focus on enhancing cloud security posture through technologies such as cloud access security brokers (CASBs), secure access service edge (SASE), and cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs). Moreover, organizations will need to navigate a constantly changing landscape of data privacy regulations and compliance requirements, requiring a proactive approach to cloud security and governance.
6. Deepfake and Synthetic Media Risks
Deepfake and Synthetic Media Risks
The proliferation of deepfake technology, which allows for the creation of highly realistic synthetic media, presents new challenges for cybersecurity and disinformation campaigns. Deepfakes can be used to create convincing forgeries of individuals, leading to potential misuse in social engineering attacks, fraud, and reputation damage.
In 2024, organizations and individuals will need to be vigilant against the risks posed by deepfake content, implementing measures such as media authentication, digital watermarking, and deepfake detection tools. Additionally, raising awareness about the existence and potential impact of deepfakes will be crucial in mitigating the spread of false information and manipulation.
7. Supply Chain Security Vulnerabilities
Supply Chain Security Vulnerabilities
The interconnected nature of global supply chains has made them prime targets for cyber attacks, as demonstrated by high-profile incidents of software supply chain compromises. In the coming years, supply chain security vulnerabilities will continue to pose significant risks to organizations, requiring a comprehensive approach to risk management and vendor security assessments.
Organizations will need to prioritize supply chain visibility, implement secure development practices, and establish mechanisms for rapid threat detection and response within their supply chain ecosystem. Collaboration and information sharing between supply chain partners will also be essential in strengthening overall resilience against supply chain attacks.
8. 5G Network Security Considerations
5G Network Security Considerations
The rollout of 5G networks brings unprecedented speed and connectivity capabilities, but it also introduces new security considerations for both mobile operators and end users. With the proliferation of connected devices and the expansion of edge computing, 5G networks will become increasingly attractive targets for cyber attacks.
In 2024, the focus on 5G network security will center on implementing robust authentication and encryption mechanisms, securing network slicing and virtualized infrastructure, and addressing emerging threats specific to 5G technology. Collaboration between network operators, technology vendors, and regulatory bodies will be crucial in establishing a secure and resilient 5G ecosystem.
9. Cybersecurity Skills Gap and Talent Shortage
Cybersecurity Skills Gap and Talent Shortage
The demand for cybersecurity professionals continues to outpace the availability of skilled talent, leading to a persistent skills gap across the industry. In 2024, addressing the cybersecurity workforce shortage will be a critical priority for organizations seeking to build and maintain effective security teams.
To bridge the skills gap, efforts to promote cybersecurity education and training, diversity and inclusion in the field, and upskilling and reskilling initiatives will be essential. Furthermore, organizations will need to explore alternative staffing models, such as managed security services and automation, to augment their internal capabilities and address resource constraints.
10. Regulatory and Geopolitical Impacts on Cybersecurity
Regulatory and Geopolitical Impacts on Cybersecurity
Changing regulatory landscapes and geopolitical tensions can have profound impacts on cybersecurity practices and threat landscapes. In 2024, organizations will need to navigate evolving data protection regulations, cross-border data transfer restrictions, and the geopolitical implications of emerging cyber threats.
This will require a proactive approach to compliance, risk assessment, and geopolitical threat intelligence, as well as strategic partnerships and engagement with regulators and government entities. By staying abreast of regulatory and geopolitical developments, organizations can adapt their cybersecurity strategies to effectively manage associated risks and compliance requirements.
| Trend/Threat | Description |
|---|---|
| AI-Powered Cyber Attacks | Adversaries are using AI to launch more sophisticated and targeted cyber attacks. |
| Ransomware Evolution | Ransomware attacks are becoming more complex, with attackers demanding larger payments and targeting critical infrastructure. |
| IoT Vulnerabilities | The increasing number of IoT devices creates new entry points for cyber attacks. |
| 5G Security Challenges | The rollout of 5G networks presents new security concerns due to increased connectivity and data transfer speeds. |
| Supply Chain Attacks | Attackers are targeting software supply chains to distribute malware to unsuspecting users. |
| Regulatory Changes | New data privacy and security regulations are impacting how organizations approach cybersecurity. |
conclusıon
Cybersecurity in 2024 will be shaped by AI-powered cyber attacks, evolving ransomware threats, IoT vulnerabilities, 5G security challenges, supply chain attacks, and regulatory changes. Organizations need to stay vigilant and adapt their cybersecurity strategies to address these emerging trends and threats.