Water scarcity is a pressing global issue that poses significant challenges to sustainable development. As the demand for fresh water continues to rise, many regions around the world are facing the threat of water scarcity, leading to serious environmental, social, and economic consequences. In light of these challenges, finding sustainable solutions to address water scarcity has become an urgent priority for governments, organizations, and communities worldwide. The need for innovative approaches to water management, conservation, and equitable distribution is paramount in ensuring the availability of this essential resource for future generations. Water Scarcity: Global Challenges And Sustainable Solutions is a critical topic that requires multidisciplinary collaboration and collective action to safeguard the world’s water resources.
Amidst the global water crisis, the concept of water security has gained increasing attention as a comprehensive framework for addressing water scarcity. Integrated water resource management, water-efficient technologies, and nature-based solutions are emerging as key strategies to enhance water security and resilience in the face of growing water scarcity challenges. Furthermore, the importance of stakeholder engagement, capacity building, and policy reforms in promoting sustainable water governance cannot be overstated. As the world continues to grapple with the complex implications of water scarcity, exploring innovative financing mechanisms and public-private partnerships is essential for driving tangible progress towards sustainable water management.
1. Understanding Water Scarcity
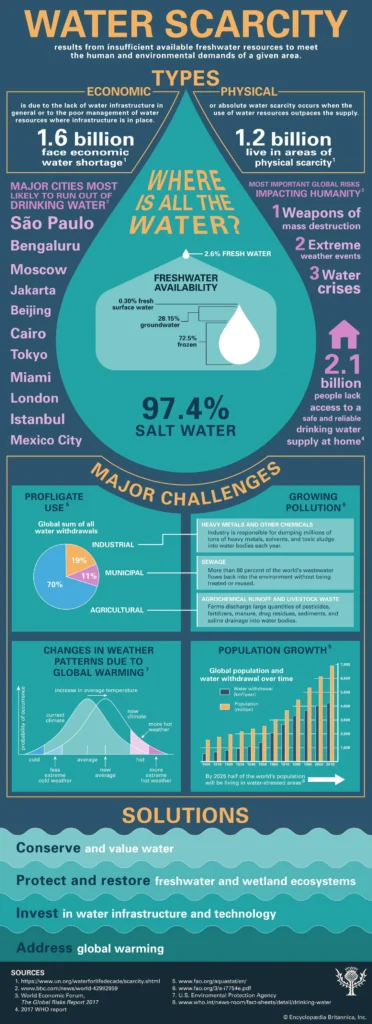
Water scarcity refers to the lack of sufficient available water resources to meet the demands of water usage within a region. This can be caused by various factors such as population growth, climate change, pollution, and inefficient water management. As a result, many regions around the world are facing challenges in accessing clean and safe water for drinking, sanitation, agriculture, and industrial activities.
Water scarcity is a complex issue that has far-reaching impacts on human health, food security, economic development, and environmental sustainability. It poses a significant threat to communities and ecosystems, leading to conflicts over water rights, migration, and ecological imbalances. Addressing water scarcity requires a holistic approach that involves sustainable water management, conservation efforts, technological innovations, and policy interventions.
2. The Global Impact of Water Scarcity
Water scarcity is a global challenge that affects both developed and developing countries, albeit in different ways. In arid and semi-arid regions, such as the Middle East and parts of Africa, water scarcity is a constant threat to livelihoods and agricultural productivity. In urban areas, rapid population growth and industrialization have put pressure on water resources, leading to shortages and water quality issues.
Furthermore, water scarcity has ripple effects on various sectors, including public health, food production, energy generation, and ecosystem stability. It exacerbates poverty, hinders economic growth, and contributes to social inequalities. The global impact of water scarcity underscores the need for collaborative efforts at the international level to address this critical issue.
3. Causes of Water Scarcity
There are several interconnected factors that contribute to water scarcity, including population growth, unsustainable water use, climate change, pollution, and inadequate infrastructure. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for water for domestic, industrial, and agricultural purposes increases, putting pressure on finite water resources.
Climate change exacerbates water scarcity by altering rainfall patterns, causing droughts and floods, and affecting the availability of water sources. Pollution from industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, and urban waste further degrades water quality, making it unsuitable for consumption and ecosystem health. Inefficient water management practices, such as over-extraction of groundwater and leaky distribution systems, also contribute to water scarcity.
4. Sustainable Solutions for Water Scarcity
Addressing water scarcity requires a combination of short-term and long-term sustainable solutions. This includes improving water efficiency in agriculture, industry, and households through the adoption of water-saving technologies and practices. Investing in water infrastructure, such as water treatment plants, distribution networks, and wastewater management systems, can help minimize water loss and ensure access to clean water.
Furthermore, promoting ecosystem conservation and watershed management is crucial for preserving natural water sources and enhancing water quality. Implementing integrated water resource management approaches that consider the social, economic, and environmental aspects of water usage can help optimize water allocation and reduce conflicts. Additionally, raising awareness about water conservation and empowering local communities to participate in water governance are essential components of sustainable solutions for water scarcity.
5. Innovations in Water Technology
Advancements in water technology play a key role in addressing water scarcity by improving water access, quality, and efficiency. Innovative solutions such as desalination, water reclamation, and rainwater harvesting enable the utilization of alternative water sources to supplement traditional freshwater supplies. Smart water management systems, including sensor-based monitoring and automated control systems, help optimize water use and detect leaks in real time.
Furthermore, the development of affordable and decentralized water treatment technologies allows communities to purify water at the point of use, reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure. Emerging technologies, such as nanomaterial-based filtration and solar-powered water pumps, offer promising solutions for providing clean water in off-grid and remote areas. Investing in research and development of water technologies is essential for creating sustainable and scalable solutions to mitigate water scarcity.
6. Policy and Governance for Water Management
Effective water governance and policy frameworks are essential for managing water resources sustainably and equitably. Governments play a critical role in establishing regulations, standards, and incentives to promote water conservation, pollution prevention, and efficient water use. Integrated water planning at the national and regional levels can help balance competing water demands and prioritize water allocation for different sectors.
International cooperation and transboundary water agreements are crucial for managing shared water resources and resolving conflicts between neighboring countries. Engaging stakeholders, including local communities, indigenous groups, and private sectors, in water decision-making processes fosters inclusive and participatory water governance. Investing in capacity building and institutional strengthening is necessary for implementing and enforcing water policies effectively.
7. Community Engagement in Water Conservation
Empowering local communities to participate in water conservation efforts is essential for creating sustainable and impactful solutions. Community-based water management initiatives, such as watershed restoration projects and water user associations, enable stakeholders to take ownership of water resources and implement tailored conservation strategies.
Educational programs and outreach activities that raise awareness about water conservation practices and the importance of preserving water ecosystems can mobilize community support for sustainable water stewardship. Involving indigenous knowledge and traditional water management practices can enrich modern approaches to water conservation and foster respect for cultural values associated with water. Building partnerships between governments, civil society organizations, and local communities strengthens collective action for addressing water scarcity at the grassroots level.
8. Business and Industry Responsibilities
Businesses and industries have a significant role to play in addressing water scarcity by adopting responsible water management practices and reducing their water footprint. Implementing water efficiency measures, such as recycling and reusing water in production processes, can minimize water consumption and wastewater generation. Conducting water risk assessments and integrating water stewardship into corporate strategies help businesses identify and address water-related challenges.
Engaging in partnerships with local communities and supporting water-related projects, such as watershed restoration and access to clean water, demonstrates corporate social responsibility and contributes to sustainable water management. Embracing transparent reporting on water usage, pollution prevention, and compliance with water regulations fosters accountability and transparency in business operations. By incorporating water sustainability into their operations, businesses can contribute to collective efforts in mitigating water scarcity.
9. Financing Water Infrastructure and Access
Investing in water infrastructure and expanding access to water services require significant financial resources, particularly in developing countries and underserved communities. Mobilizing public and private investments in water projects, such as building water treatment plants, expanding water distribution networks, and improving sanitation facilities, is essential for enhancing water security.
Exploring innovative financing mechanisms, including public-private partnerships, water bonds, and impact investment funds, can leverage capital for sustainable water infrastructure development. Microfinance and community-based financing models enable individuals and small-scale enterprises to invest in water technologies and services, promoting financial inclusion and local entrepreneurship in the water sector. Additionally, ensuring affordability and equity in water pricing and tariff structures is crucial for providing universal access to water while securing the financial sustainability of water utilities.
10. Education and Advocacy for Water Sustainability
Education and advocacy efforts play a vital role in promoting water sustainability by fostering a culture of responsible water usage and environmental stewardship. Integrating water conservation and environmental education into school curricula cultivates a generation of informed and proactive citizens who value and protect water resources.
Raising public awareness through campaigns, media outreach, and community events highlights the interconnectedness of water with human well-being, ecosystems, and the economy. Advocating for policies that prioritize water sustainability, climate resilience, and equitable water access amplifies the collective voice for positive change in water governance and management. Engaging in public dialogue and knowledge sharing platforms creates opportunities for collaboration and innovation in advancing water sustainability goals at local, national, and global levels.
| Issue | Impact |
|---|---|
| Increasing population | Higher demand for water resources |
| Climate change | Altered precipitation patterns leading to droughts or floods |
| Water pollution | Contaminated water sources affecting human health |
| Water wastage | Reduced availability of clean water for essential needs |
conclusıon
Water scarcity is a pressing global issue driven by factors such as increasing population, climate change, water pollution, and water wastage. This challenge has significant impacts on human health, agriculture, and the environment. However, sustainable solutions such as water conservation, improved water management, and investment in clean water technologies can help address this issue and ensure a more secure water future for all.