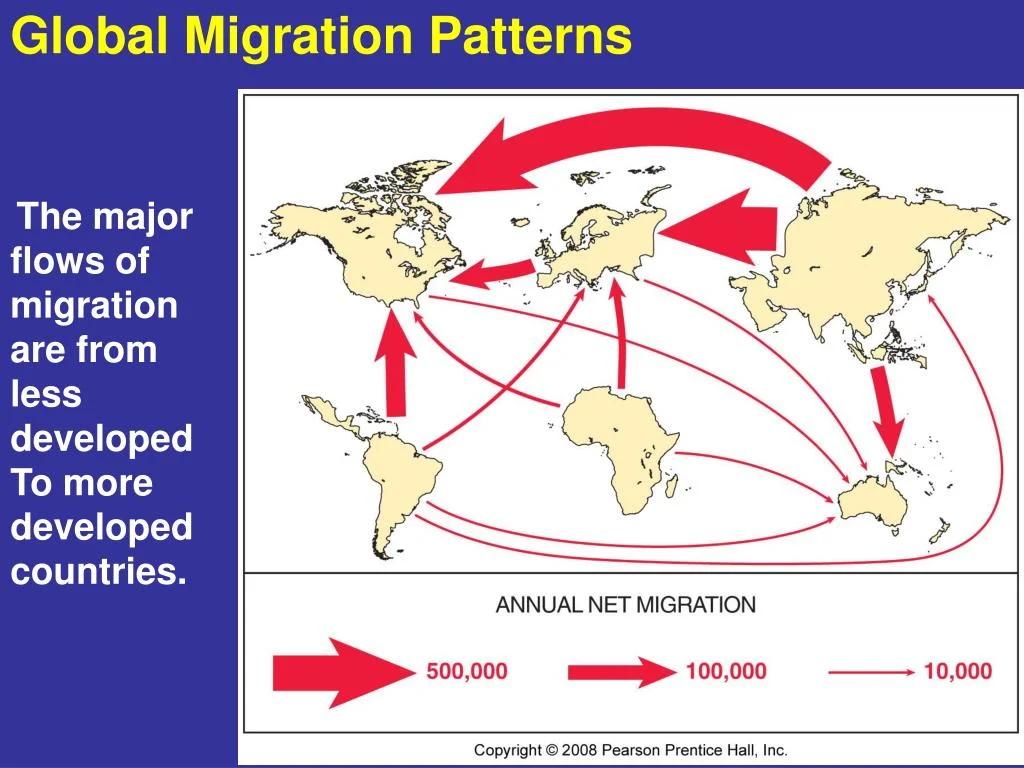
Migration Patterns: Understanding The Causes And Effects Of Global Movement is a complex and multifaceted topic that has garnered increasing attention in recent years. The movement of people across borders, whether for economic, political, or environmental reasons, has significant impacts on both the source and destination countries. Understanding the reasons behind migration patterns and their effects is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and the general public alike.
The global movement of people, also known as human migration, has been a subject of great interest due to its impact on various aspects of society. The causes of migration can range from economic opportunities and political instability to environmental factors such as climate change and natural disasters. These movements can have profound effects on the demographics, economies, and cultures of both the origin and destination countries. Therefore, understanding the underlying reasons and consequences of migration patterns is essential for developing effective policies and strategies to address the challenges and opportunities associated with this global phenomenon.
1. Economic Factors Influencing Migration Patterns
Migration is often driven by economic factors, as people seek better employment opportunities and higher wages in other countries. In many cases, individuals and families are compelled to leave their home countries due to poverty, lack of job prospects, or economic instability. They may be drawn to countries with stronger economies, where they believe they can secure a better future for themselves and their families. Additionally, global economic disparities can create a demand for migrant labor in certain industries, leading to patterns of migration from less affluent regions to more prosperous ones.
Furthermore, economic crises, such as recessions or currency devaluations, can force people to seek opportunities abroad. This was evident in the European debt crisis, which led to significant migration from countries like Greece and Spain to more stable economies within the European Union. Ultimately, economic factors play a significant role in shaping migration patterns, as individuals and families pursue better economic prospects and seek to escape economic hardship in their home countries.
2. Political and Social Factors Impacting Migration
Political instability, persecution, and human rights abuses can also drive migration as people seek safety and freedom in other countries. Individuals may flee conflict zones, repressive regimes, or areas where they face discrimination or persecution based on their ethnicity, religion, or political beliefs. The desire for political asylum and the need to escape from war-torn regions or oppressive governments can lead to significant refugee movements and patterns of migration to more stable and democratic countries.
Social factors, such as access to education, healthcare, and social services, can also influence migration patterns. People may be drawn to countries with strong social welfare systems and opportunities for personal and professional development. Additionally, family reunification and the desire to be with loved ones who have already migrated can be powerful social factors driving migration. Overall, political and social factors can profoundly impact migration patterns, as individuals seek safety, freedom, and a better quality of life in other parts of the world.
3. Environmental Causes of Migration
Environmental factors, including natural disasters, climate change, and environmental degradation, can compel people to leave their homes and seek refuge in other regions or countries. Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and diminishing natural resources can disrupt livelihoods and lead to forced migration. For example, island nations like Tuvalu and the Maldives face the existential threat of being submerged due to sea-level rise, prompting discussions of planned relocation and migration to other countries.
Furthermore, environmental degradation, such as deforestation, desertification, and soil erosion, can undermine agricultural productivity and contribute to rural-to-urban migration as people seek alternative livelihoods in urban centers. Climate change-induced phenomena, such as droughts and floods, can also displace communities and lead to patterns of internal and international migration. As the global climate crisis intensifies, environmental factors are becoming increasingly significant in shaping migration patterns and influencing the movement of people across borders.
4. Cultural and Demographic Influences on Migration
Cultural and demographic factors can also play a role in shaping migration patterns. The desire to experience different cultures, pursue educational opportunities, or be part of a diaspora community can motivate people to migrate to other countries. Additionally, demographic trends, such as aging populations in some countries and a need for labor in others, can drive migration patterns as people seek to address labor shortages or reunite with family members living abroad.
Diaspora communities, formed by historical patterns of migration, can also facilitate ongoing migration as individuals seek to join relatives and communities already established in other countries. Cultural and demographic influences on migration are complex and multifaceted, reflecting the diverse motivations and aspirations of people as they seek to build their lives in new and unfamiliar environments.
5. Economic Impact of Migration on Sending and Receiving Countries
The movement of people across borders can have significant economic impacts on both sending and receiving countries. In sending countries, migration can alleviate unemployment and reduce pressure on social services as people seek opportunities abroad. However, it can also lead to a loss of skilled workers, known as “brain drain,” and contribute to labor shortages in key industries, particularly in sectors like healthcare and education.
In receiving countries, migration can contribute to economic growth by providing a workforce for essential industries and addressing labor shortages. Migrants often take on jobs that native-born workers are unwilling to do, sustaining critical sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and hospitality. Additionally, migrants contribute to consumer spending, entrepreneurship, and innovation, enriching the economic fabric of their new communities. Overall, the economic impact of migration is complex and multifaceted, with both positive and negative effects for sending and receiving countries.
6. Social and Cultural Transformations Due to Migration
Migration can lead to social and cultural transformations in both sending and receiving societies. In sending countries, the departure of individuals and families can impact community structures, family dynamics, and traditional practices. The absence of working-age adults and young people can alter local economies and social networks, while also creating transnational family ties and connections across borders.
In receiving countries, migration contributes to cultural diversity, enriching societies with new languages, traditions, and perspectives. However, it can also lead to social tensions and challenges related to integration, as different cultural groups navigate coexistence and adaptation in diverse communities. Ultimately, migration has the power to reshape social and cultural landscapes, fostering intercultural dialogue and the exchange of ideas while also posing integration challenges for both migrants and host communities.
7. Legal and Policy Frameworks Shaping Migration Patterns
Legal and policy frameworks established by governments and international organizations play a critical role in shaping migration patterns. Immigration laws, visa regulations, and refugee policies determine who can enter a country, under what circumstances, and for how long. These legal frameworks can influence the flow of migrants, the treatment of refugees, and the integration of newcomers into societies.
Furthermore, international agreements and conventions, such as the United Nations Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration, seek to coordinate global responses to migration and establish principles for protecting the rights of migrants. However, the implementation and enforcement of migration-related laws and policies can vary widely between countries, leading to disparities in the treatment of migrants and the effectiveness of migration management. Legal and policy frameworks are central to understanding and addressing migration patterns, as they define the parameters within which migration occurs and the rights afforded to individuals on the move.
8. The Role of Technology in Shaping Migration
Advancements in technology have significantly impacted migration patterns, facilitating the movement of people across borders and enabling transnational connections. Digital communication tools, such as social media and messaging apps, allow migrants to stay connected with their families and communities, even across great distances. Additionally, online platforms and job portals have transformed the process of searching for employment abroad, making it easier for individuals to explore opportunities in other countries.
Furthermore, technological innovations in transportation have reduced the time and cost of travel, making international migration more accessible to a larger number of people. From affordable air travel to online booking platforms, technology has lowered barriers to mobility and expanded the possibilities for global movement. However, technology also presents challenges, such as the spread of misinformation about migration and the exploitation of migrants through online recruitment scams. The role of technology in shaping migration is complex, with both positive and negative implications for individuals on the move.
9. Humanitarian Responses to Migration Crises
Humanitarian responses to migration crises, such as large-scale refugee movements and natural disaster-induced displacement, have a profound impact on migration patterns. International organizations, non-governmental agencies, and host countries often mobilize to provide assistance and protection to displaced populations, offering shelter, food, medical care, and legal support. Humanitarian responses can influence the trajectories of migration, as they determine the accessibility of aid, asylum, and resettlement options for those in need.
Moreover, humanitarian interventions can shape public perceptions of migration, influencing attitudes towards refugees and migrants. The provision of humanitarian aid and the reception of displaced populations can vary widely between countries, reflecting different approaches to addressing migration crises and supporting vulnerable individuals and families. Humanitarian responses are essential in addressing the immediate needs of migrants and refugees, while also influencing the long-term patterns of migration and the dynamics of global movement.
10. The Future of Migration in a Globalized World
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, migration is likely to remain a prominent feature of the global landscape. Economic, political, environmental, and social factors will continue to drive patterns of migration, shaping the movement of people across borders. Global efforts to address migration-related challenges, such as forced displacement, labor migration, and integration, will be essential in shaping the future of migration.
Furthermore, the impacts of climate change, technological advancements, and demographic shifts will intersect with migration dynamics, presenting both opportunities and complexities for individuals and societies on the move. Understanding the causes and effects of migration, as well as the evolving legal and policy frameworks governing migration, will be crucial in navigating the complexities of global movement in the 21st century.
Migration Patterns: Understanding The Causes And Effects Of Global Movement
Migration is a global phenomenon that involves the movement of people from one place to another for various reasons. This movement can be caused by push factors such as conflict, poverty, and lack of opportunities, or pull factors such as better economic prospects, political stability, and family reunification. The effects of migration are diverse and can impact both the sending and receiving countries in terms of demographics, labor markets, cultural diversity, and social dynamics. Understanding the causes and effects of global movement is crucial for policymakers and societies to develop effective strategies for managing and benefiting from migration.
| Causes of Migration | Effects of Migration |
|---|---|
| Push Factors | Demographic changes |
| Pull Factors | Labor market dynamics |
| Environmental factors | Cultural diversity |
| Conflict and persecution | Social integration |
| Economic opportunities | Remittances |
conclusıon
Migration is a complex phenomenon driven by a combination of push and pull factors, and its effects are varied and far-reaching. Understanding the causes and effects of global movement is essential for creating policies that can address the challenges and harness the potential benefits of migration for both sending and receiving countries.