In recent years, the development of autonomous vehicles has been a hot topic in the automotive industry. The road to self-driving cars has been paved with technological advancements and intense competition among leading companies. Autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving cars, have the potential to revolutionize transportation by providing safer and more efficient means of travel. The integration of artificial intelligence and advanced sensors allows these vehicles to navigate and operate without human intervention, promising a new era in mobility.
As the world eagerly anticipates the widespread adoption of self-driving cars, there is a growing curiosity about the potential impact on road safety, traffic congestion, and urban planning. The concept of autonomous vehicles has sparked interest in alternative modes of transportation and the future of mobility. Questions about the ethical and legal implications of self-driving cars have also emerged, as society grapples with the idea of relinquishing control to machines on the road. Additionally, the economic and environmental effects of autonomous vehicles are subjects of great interest, as they have the potential to reshape industries and reduce carbon emissions.
1. The Evolution of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving cars, have been a topic of great interest and innovation in recent years. The concept of autonomous vehicles dates back to the 1920s, but it wasn’t until the 1980s and 1990s that significant advancements in technology paved the way for the development of self-driving cars. Today, autonomous vehicles are equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence systems that allow them to navigate roads and make decisions without human intervention.
The evolution of autonomous vehicles has been driven by the goal of increasing road safety, reducing traffic congestion, and providing mobility solutions for individuals who are unable to drive themselves. As technology continues to advance, autonomous vehicles are expected to become more prevalent on the roads, reshaping the way we think about transportation and urban planning.
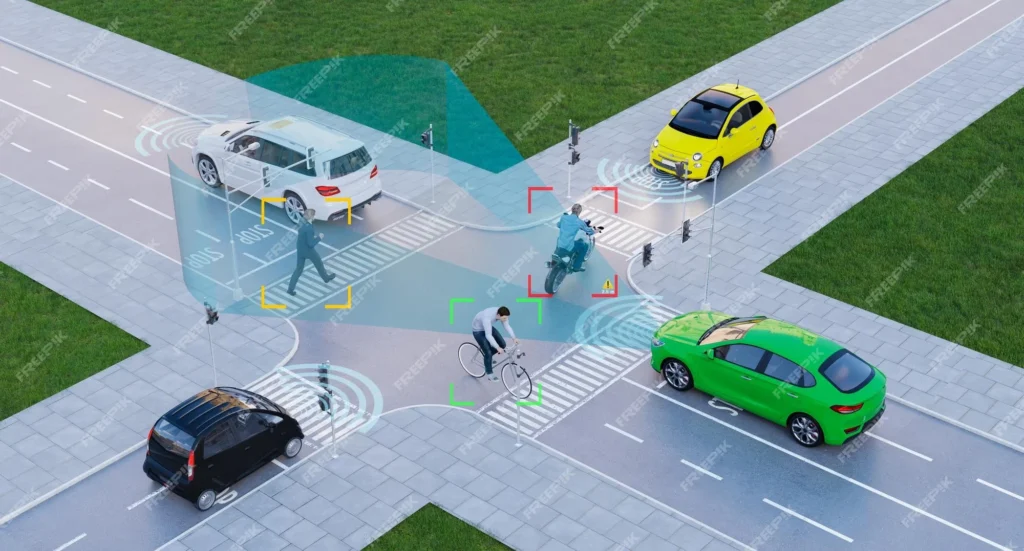
2. The Technology Behind Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles rely on a complex network of technologies to navigate the roads and make decisions in real time. These technologies include LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors, radar, cameras, and GPS systems, which provide the vehicle with a 360-degree view of its surroundings. In addition, artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are used to interpret and react to the data collected by these sensors, allowing the vehicle to make decisions such as changing lanes, navigating traffic, and avoiding obstacles.
The development of autonomous vehicles also involves extensive testing and simulation to ensure their safety and reliability. Companies and researchers in the field are constantly refining and improving the technology to address challenges such as unpredictable road conditions, pedestrian interactions, and cybersecurity threats.
3. The Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to offer numerous benefits to society. One of the primary advantages is the potential to reduce traffic accidents and fatalities, as human error is a leading cause of road accidents. In addition, self-driving cars have the potential to improve traffic flow and reduce congestion, as they can communicate with each other to optimize speed and spacing on the road.
Autonomous vehicles also have the potential to increase mobility for individuals who are unable to drive due to age, disability, or other reasons. They could provide a new form of transportation for those who are unable to access traditional modes of transportation, improving their quality of life and independence. Furthermore, self-driving cars have the potential to reduce the environmental impact of transportation by optimizing routes and reducing fuel consumption.
4. Legal and Regulatory Challenges
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles faces several legal and regulatory challenges. One of the primary concerns is the need to establish a clear legal framework for determining liability in the event of accidents involving autonomous vehicles. Additionally, there are questions surrounding data privacy and cybersecurity, as self-driving cars rely on extensive data collection and communication systems.
Regulators also face the challenge of ensuring that autonomous vehicles meet safety standards and are capable of operating in a wide range of real-world conditions. This requires the development of comprehensive testing and certification processes to ensure the safety and reliability of self-driving cars before they can be deployed on public roads.
5. The Impact on Urban Planning and Infrastructure
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles is expected to have a significant impact on urban planning and infrastructure. With the potential to reduce the need for parking spaces and optimize traffic flow, self-driving cars could reshape the design of urban areas, leading to more efficient land use and reduced congestion. In addition, the development of autonomous public transportation systems could offer new opportunities for urban mobility and accessibility.
However, the integration of autonomous vehicles into existing infrastructure presents challenges, such as the need to upgrade roads and traffic management systems to accommodate self-driving cars. Furthermore, planners and policymakers will need to consider the potential social and economic impacts of autonomous vehicles on public transportation systems and urban development.
6. The Future of Autonomous Vehicles
The future of autonomous vehicles holds promise for continued innovation and widespread adoption. As technology continues to advance, self-driving cars are expected to become more affordable and accessible, leading to greater adoption by consumers and businesses. In addition, the development of autonomous public transportation systems, such as self-driving buses and shuttles, could offer new solutions for urban mobility and accessibility.
Furthermore, the integration of autonomous vehicles with emerging technologies, such as electric and connected vehicles, has the potential to revolutionize the transportation industry and reduce its environmental impact. However, the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles will require continued collaboration between industry stakeholders, regulators, and policymakers to address technical, legal, and societal challenges.
7. Ethical Considerations in Autonomous Vehicles
The development of autonomous vehicles raises important ethical considerations, particularly in the context of decision-making in potentially harmful situations. For example, self-driving cars may face dilemmas in situations where they must choose between different courses of action, such as swerving to avoid a pedestrian or protecting the safety of the vehicle occupants. Resolving these ethical dilemmas requires careful consideration of moral principles and the development of ethical decision-making frameworks for autonomous vehicles.
In addition, the deployment of autonomous vehicles raises questions about job displacement in the transportation industry, as well as the potential impact on social equity and accessibility. Addressing these ethical considerations requires collaboration between industry, policymakers, and ethicists to ensure that the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles prioritize the safety and well-being of society as a whole.
8. Public Perception and Acceptance
Public perception and acceptance of autonomous vehicles play a crucial role in their widespread adoption and deployment. Building trust and confidence in the safety and reliability of self-driving cars is essential to overcome skepticism and concerns about new technology. This requires transparent communication from industry stakeholders about the capabilities and limitations of autonomous vehicles, as well as efforts to address public concerns about privacy, cybersecurity, and job displacement.
Furthermore, public education and awareness campaigns can help to familiarize individuals with the potential benefits of autonomous vehicles and alleviate fears about their safety and impact on society. By engaging with communities and stakeholders, industry and government can work together to address public concerns and ensure that the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles align with the needs and values of society.
9. The Role of Government and Industry Collaboration
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles requires collaboration between government and industry stakeholders to address technical, legal, and societal challenges. Government agencies play a critical role in establishing a clear regulatory framework for the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles, including safety standards, liability regulations, and data privacy laws.
Industry stakeholders, including automakers, technology companies, and transportation providers, play a key role in driving innovation and investment in autonomous vehicles. Collaboration between government and industry can help to ensure that the development of autonomous vehicles aligns with public priorities and addresses societal needs, such as road safety, accessibility, and environmental sustainability.
10. The Global Landscape of Autonomous Vehicles
The development and deployment of autonomous vehicles are taking place on a global scale, with countries and regions around the world investing in research, development, and testing of self-driving cars. In addition to technological advancements, differences in legal and regulatory frameworks, as well as societal attitudes and infrastructure, contribute to a diverse global landscape for autonomous vehicles.
Countries such as the United States, China, and European nations are at the forefront of autonomous vehicle development, with significant investments and pilot programs aimed at advancing the technology and exploring its potential impact. As the global landscape of autonomous vehicles continues to evolve, international collaboration and knowledge sharing will play a crucial role in addressing common challenges and ensuring the safe and responsible deployment of self-driving cars.
| Level of Automation | Description |
|---|---|
| Level 0: No Automation | The driver is in complete control of the vehicle at all times. |
| Level 1: Driver Assistance | Some driving assistance features, such as cruise control, are available. |
| Level 2: Partial Automation | The vehicle can control both steering and acceleration, but the driver must remain engaged and monitor the environment at all times. |
| Level 3: Conditional Automation | The vehicle can manage most aspects of driving, but the driver may need to intervene in certain situations. |
| Level 4: High Automation | The vehicle is capable of performing all driving functions under certain conditions, with no human intervention required. |
| Level 5: Full Automation | The vehicle is fully autonomous and requires no human input for any driving tasks. |
Autonomous Vehicles: The Road To Self-Driving Cars describes the different levels of automation in vehicles, ranging from no automation to full automation. As technology advances, the goal is to achieve full automation, where vehicles can operate without any human input for driving tasks. This has the potential to revolutionize transportation and improve road safety.