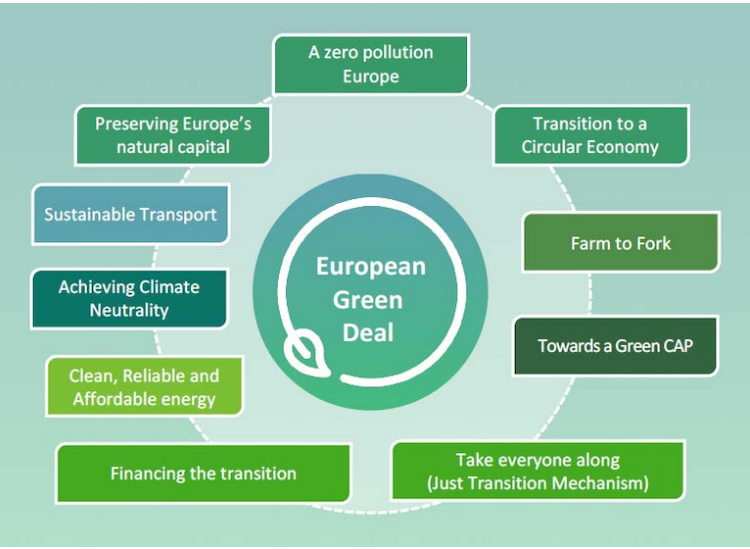
The European Union has taken a significant step forward in the fight against climate change by signing a new climate pact aimed at reducing carbon emissions. This landmark agreement not only underscores the EU’s commitment to sustainability but also sets a precedent for global environmental policies. As nations grapple with the urgent need to address climate change, the EU’s initiative serves as a beacon of hope, showcasing the potential for collaborative efforts to mitigate the effects of global warming.
In this article, we will delve into the key components of the EU’s new climate pact, exploring its ambitious targets and the strategies that will be employed to achieve them. Readers will gain insights into how this agreement will influence various sectors, from energy production to transportation, and the role of innovation in driving sustainable practices. Furthermore, we will discuss the potential economic impacts and the importance of international cooperation in achieving these goals.
As we navigate through the details of this pivotal agreement, you will discover how the EU’s actions could inspire other regions to adopt similar measures, fostering a global movement towards a greener future. Stay with us as we unpack the implications of the EU’s new climate pact and what it means for our planet’s health and future generations. Your understanding of climate action and its significance in today’s world will be enriched as we explore these critical topics together.
The European Union has taken a significant step forward in the fight against climate change by signing a new climate pact aimed at reducing carbon emissions. This agreement is crucial for achieving the EU’s long-term sustainability goals and addressing the urgent need for action against global warming.
Overview of the New Climate Pact
The new climate pact outlines specific targets for carbon emission reductions across various sectors, including transportation, energy, and agriculture. The EU aims to achieve a significant decrease in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030, with a long-term goal of becoming climate-neutral by 2050. This ambitious plan reflects the EU’s commitment to international climate agreements and its leadership role in global environmental policy.
In addition to setting reduction targets, the pact includes provisions for monitoring progress and ensuring compliance among member states. This framework is essential for maintaining accountability and fostering cooperation among nations as they work towards shared climate goals.
Economic Implications of the Pact
The economic impact of the new climate pact is a critical consideration for EU member states. Transitioning to a low-carbon economy presents both challenges and opportunities. While some industries may face increased costs due to stricter regulations, others, particularly those focused on renewable energy and green technologies, are likely to benefit from new investments and job creation.
Moreover, the pact encourages innovation and research in sustainable practices, which can lead to long-term economic growth. By investing in green technologies, the EU can position itself as a leader in the global market for sustainable solutions, ultimately driving economic resilience in the face of climate change.
Role of Renewable Energy in Emission Reduction
Renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, play a pivotal role in the EU’s strategy to reduce carbon emissions. The new climate pact emphasizes the need to transition away from fossil fuels and invest in clean energy alternatives. This shift not only helps to lower emissions but also enhances energy security and reduces dependence on imported fuels.
As part of the pact, member states are encouraged to increase their renewable energy capacity and implement policies that support the development of sustainable energy infrastructure. This includes incentives for businesses and households to adopt renewable technologies, which can significantly contribute to the EU’s overall emission reduction targets.
Impact on Transportation Sector
The transportation sector is one of the largest contributors to carbon emissions in the EU. The new climate pact addresses this issue by promoting the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the development of sustainable public transport systems. By investing in EV infrastructure and encouraging the use of public transport, the EU aims to significantly reduce emissions from this sector.
Additionally, the pact includes measures to improve fuel efficiency and promote alternative fuels, such as biofuels and hydrogen. These initiatives are essential for achieving the EU’s climate goals and ensuring a sustainable future for transportation.
Public Engagement and Awareness
Public engagement is crucial for the success of the new climate pact. The EU recognizes that raising awareness about climate change and its impacts is essential for fostering a culture of sustainability. Educational campaigns and community initiatives are being implemented to inform citizens about the importance of reducing carbon emissions and adopting sustainable practices.
By involving the public in climate action, the EU aims to create a sense of shared responsibility and encourage individuals to make environmentally conscious choices in their daily lives. This grassroots approach can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the pact and contribute to achieving the EU’s climate objectives.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
While the new climate pact represents a significant step forward, it also presents challenges that must be addressed. Ensuring compliance among member states, managing the economic transition, and adapting to the impacts of climate change are all critical issues that require ongoing attention and collaboration.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth. By embracing sustainable practices and investing in green technologies, the EU can lead the way in the global transition to a low-carbon economy, ultimately benefiting both the environment and the economy.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Objective | The EU Climate Pact aims to significantly reduce carbon emissions across member states to combat climate change and promote sustainability. |
| Key Targets | To achieve a minimum of 55% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. |
| Strategies | Implementation of renewable energy sources, energy efficiency improvements, and promotion of sustainable transportation. |
| Involvement | Encourages participation from local governments, businesses, and citizens to adopt eco-friendly practices. |
| Funding | Allocation of financial resources to support green projects and initiatives across the EU. |
| Monitoring | Regular assessments and reports on progress towards emission reduction targets to ensure accountability. |
| International Cooperation | Collaboration with non-EU countries to share best practices and technologies for reducing carbon footprints. |