The global chip shortage continues to impact industries across the globe, creating significant challenges for manufacturers and consumers alike. As technology becomes increasingly integrated into our daily lives, the demand for semiconductors has surged, leading to a supply chain crisis that has affected everything from automotive production to consumer electronics. This shortage has not only disrupted production schedules but has also driven up prices, leaving many companies scrambling to adapt to the new normal.
In this article, we will delve into the root causes of the global chip shortage, examining factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical tensions, and the rapid growth of emerging technologies. We will also explore how different sectors, including automotive, healthcare, and telecommunications, are navigating these challenges and what strategies they are employing to mitigate the impact. Furthermore, we will discuss the potential long-term implications of this shortage on innovation and market dynamics.
As we unpack the complexities of the global chip shortage, you will gain insights into how this crisis is reshaping industries and what it means for the future of technology. Whether you are a business leader, a tech enthusiast, or simply curious about the state of the semiconductor market, this article will provide you with valuable information and a deeper understanding of the ongoing situation. Stay with us as we explore the multifaceted effects of this critical issue and what lies ahead.
Overview of the Global Chip Shortage
The global chip shortage has emerged as a significant issue affecting various industries, particularly automotive, consumer electronics, and telecommunications. This shortage is primarily driven by the COVID-19 pandemic, which disrupted supply chains and increased demand for electronic devices as remote work and online activities surged. As a result, manufacturers are struggling to meet the rising demand for semiconductors, leading to production delays and increased costs.
In addition to the pandemic, geopolitical tensions and natural disasters have further exacerbated the situation. For instance, the fire at a major semiconductor plant in Japan and the drought affecting chip production in Taiwan have highlighted the fragility of the global supply chain. Understanding the root causes of the chip shortage is essential for industries to navigate these challenges effectively.
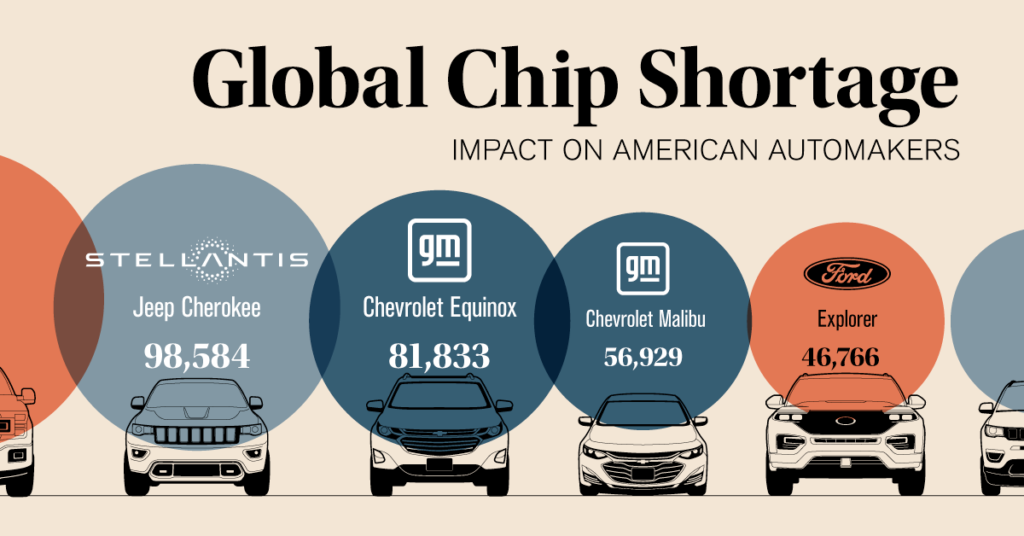
Impact on the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has been one of the hardest hit by the global chip shortage. Many modern vehicles rely on a multitude of chips for essential functions, including engine control, safety features, and infotainment systems. As a result, automakers have been forced to halt production or reduce the number of vehicles manufactured, leading to significant financial losses.
In response to the shortage, some manufacturers are reevaluating their supply chain strategies, seeking to diversify their sources of semiconductors and invest in domestic production capabilities. This shift may lead to a more resilient automotive industry in the long run, but the immediate effects of the chip shortage continue to pose challenges for both manufacturers and consumers.
Effects on Consumer Electronics
The consumer electronics sector has also felt the impact of the global chip shortage. With the increased demand for devices such as smartphones, laptops, and gaming consoles, manufacturers are struggling to keep up with production. This has resulted in longer wait times for consumers and inflated prices for popular products.
Companies are now prioritizing the production of high-demand items, often at the expense of less popular products. This shift in focus may lead to a temporary imbalance in the market, as consumers find it increasingly difficult to purchase certain electronics. As the industry adapts, it will be crucial for manufacturers to find innovative solutions to mitigate the effects of the chip shortage.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Solutions
The global chip shortage has exposed vulnerabilities in the supply chain, prompting industries to seek solutions to mitigate future disruptions. Companies are increasingly looking to establish closer relationships with semiconductor manufacturers and invest in local production facilities to reduce reliance on overseas suppliers.
Additionally, some industries are exploring alternative materials and technologies to create chips, which could help alleviate the pressure on traditional semiconductor manufacturing. By diversifying their supply chains and investing in new technologies, companies can better prepare for future challenges and ensure a more stable supply of critical components.
Future Trends in Semiconductor Manufacturing
The semiconductor industry is undergoing significant changes in response to the global chip shortage. Companies are ramping up investments in research and development to enhance manufacturing capabilities and increase production capacity. This includes the development of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 5nm and 3nm processes, which promise to deliver more powerful and efficient chips.
Moreover, governments around the world are recognizing the strategic importance of semiconductor manufacturing and are implementing policies to support domestic production. This trend may lead to a more balanced global semiconductor landscape, reducing the risk of future shortages and ensuring a steady supply of chips for various industries.
Conclusion: Navigating the Chip Shortage
The global chip shortage continues to impact industries across the board, from automotive to consumer electronics. As companies grapple with the challenges posed by this shortage, it is essential for them to adapt their strategies and invest in more resilient supply chains. By fostering innovation and collaboration within the semiconductor industry, businesses can work towards a more stable future.
Ultimately, the lessons learned from the current chip shortage will shape the future of manufacturing and supply chain management. As industries evolve, they must remain vigilant and proactive in addressing potential disruptions to ensure continued growth and success.
| Industry | Impact | Causes | Future Outlook |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production delays, reduced vehicle availability, increased prices | Increased demand for electronics, factory shutdowns due to COVID-19 | Expected recovery in 2023, but challenges may persist |
| Consumer Electronics | Shortages of smartphones, laptops, and gaming consoles | High demand during pandemic, supply chain disruptions | Gradual improvement as production ramps up |
| Healthcare | Delays in medical device production, impacting patient care | Increased demand for medical technology, supply chain issues | Long-term investments in domestic manufacturing may help |
| Telecommunications | Slow rollout of 5G infrastructure, delays in network upgrades | High demand for network equipment, chip production constraints | Potential for stabilization as new fabs come online |
| Industrial Equipment | Production slowdowns, increased costs for machinery | Global supply chain disruptions, increased demand for automation | Recovery expected as supply chains normalize |