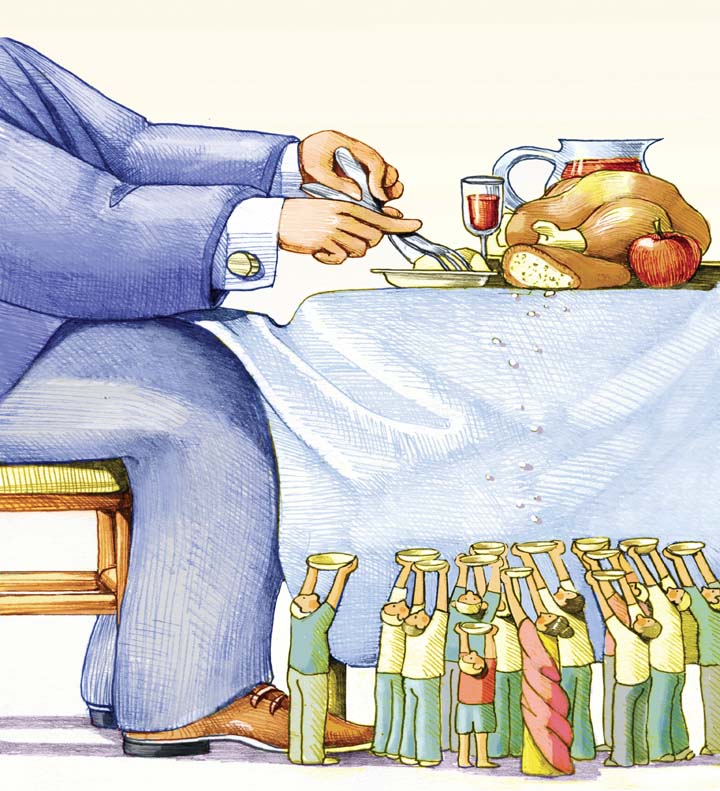
Global health inequality remains one of the most pressing challenges of our time, highlighting the stark disparities in health outcomes between rich and poor nations. This issue encompasses a range of factors, including access to healthcare, economic stability, and social determinants of health. As we delve into the complexities of global health inequality, we will explore the underlying causes and the urgent need for collaborative efforts to bridge this gap. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for fostering a healthier, more equitable world.
In the following sections, we will examine the various dimensions of global health inequality, including the impact of poverty, education, and infrastructure on health outcomes. We will also discuss innovative solutions and successful case studies that demonstrate how nations can work together to improve health equity. By shedding light on these critical aspects, we aim to inspire action and encourage readers to engage in meaningful discussions about health disparities.
As you continue reading, you will gain insights into the role of international organizations, governments, and communities in addressing health inequalities. We will highlight the importance of sustainable development goals and the need for a collective approach to ensure that everyone, regardless of their socioeconomic status, has access to quality healthcare. Join us on this journey to understand and combat global health inequality, and discover how you can contribute to bridging the gap between rich and poor nations.
Global health inequality is a pressing issue that affects millions of people worldwide. The disparity in health outcomes between rich and poor nations is stark, with wealthier countries enjoying better healthcare systems, access to medical resources, and overall health indicators. This article explores various aspects of this inequality and discusses potential solutions to bridge the gap.
Understanding Health Inequality
Health inequality refers to the differences in health status or in the distribution of health determinants between different population groups. These disparities can be influenced by various factors, including socioeconomic status, education, and access to healthcare. In many low-income countries, the lack of resources and infrastructure leads to higher rates of disease and mortality.
Moreover, health inequality is not just a problem in developing nations; it also exists within wealthy countries. Marginalized communities often face barriers to accessing quality healthcare, resulting in significant health disparities. Understanding the root causes of these inequalities is crucial for developing effective interventions.
The Role of Economic Factors
Economic factors play a significant role in health inequality. Wealthier nations can invest more in healthcare infrastructure, research, and technology, leading to better health outcomes. In contrast, poorer nations often struggle with limited resources, which hampers their ability to provide adequate healthcare services.
Additionally, economic stability influences public health policies. Countries with strong economies can implement comprehensive health programs, while those with weaker economies may prioritize other areas, leaving health services underfunded. Addressing these economic disparities is essential for improving global health equity.
Access to Healthcare Services
Access to healthcare services is a critical determinant of health outcomes. In many low-income countries, healthcare facilities are scarce, and those that exist may lack essential supplies and trained personnel. This lack of access leads to preventable diseases and higher mortality rates.
In contrast, individuals in wealthier nations typically have better access to a range of healthcare services, including preventive care, specialist treatments, and advanced medical technologies. Bridging the gap in access to healthcare is vital for reducing health disparities globally.
Education and Health Literacy
Education is closely linked to health outcomes. Higher levels of education often correlate with better health literacy, enabling individuals to make informed health choices. In many low-income countries, limited access to education contributes to poor health outcomes and a lack of awareness about health issues.
Improving education and health literacy can empower communities to take charge of their health, leading to better health practices and outcomes. Initiatives that focus on education can play a significant role in bridging the health gap between rich and poor nations.
The Impact of Globalization
Globalization has both positive and negative effects on health inequality. On one hand, it can facilitate the sharing of medical knowledge and resources across borders. On the other hand, it can exacerbate inequalities by prioritizing profit over health in poorer nations.
For instance, multinational pharmaceutical companies may focus on markets in wealthier countries, leaving low-income nations with limited access to essential medications. Addressing the challenges posed by globalization is crucial for ensuring equitable health outcomes worldwide.
The Role of International Aid
International aid plays a significant role in addressing health disparities between nations. Many low-income countries rely on foreign aid to support their healthcare systems. However, the effectiveness of aid can vary, and there are ongoing debates about the best approaches to delivering assistance.
To be effective, international aid must be targeted and sustainable, focusing on building local capacity rather than creating dependency. Collaborative efforts between donor and recipient countries can lead to more equitable health outcomes.
Innovations in Healthcare Delivery
Innovations in healthcare delivery, such as telemedicine and mobile health technologies, have the potential to bridge the gap in health inequality. These technologies can improve access to healthcare services, especially in remote and underserved areas.
By leveraging technology, healthcare providers can reach more patients and deliver essential services efficiently. Investing in innovative solutions can help address some of the systemic barriers that contribute to health disparities.
Policy Recommendations for Bridging the Gap
To effectively bridge the health gap between rich and poor nations, comprehensive policy changes are necessary. Governments must prioritize health equity in their agendas, ensuring that resources are allocated to underserved populations.
Additionally, international collaboration is essential for addressing global health challenges. By working together, nations can share best practices, resources, and knowledge to create a more equitable health landscape. Implementing these policy recommendations can lead to significant improvements in global health outcomes.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Global health inequality refers to the disparities in health status and access to healthcare between rich and poor nations. |
| Causes | Factors include economic disparities, lack of access to education, inadequate healthcare infrastructure, and social determinants of health. |
| Impact on Health | Health inequalities lead to higher rates of disease, lower life expectancy, and increased mortality in poorer nations. |
| Examples | Countries in Sub-Saharan Africa face higher rates of infectious diseases compared to wealthier nations, which have better healthcare systems. |
| Bridging the Gap | Strategies include increasing funding for healthcare, improving education, and fostering international partnerships to share resources and knowledge. |
| Role of Organizations | International organizations like WHO and NGOs play a crucial role in addressing health inequalities through programs and funding. |
| Future Directions | Focus on sustainable development, equitable healthcare access, and addressing social determinants to reduce health disparities. |