The phenomenon of global population growth is a pressing issue that continues to shape our world in profound ways. As we approach 2024, understanding the trends and challenges associated with this growth becomes increasingly vital. With the global population projected to reach approximately 8.5 billion by 2030, the implications for resources, urbanization, and environmental sustainability are more significant than ever. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of global population growth, highlighting key statistics and trends that will define the coming years.
In the following sections, we will explore the driving forces behind population growth, including fertility rates, migration patterns, and the impact of healthcare advancements. Additionally, we will examine the challenges that arise from this growth, such as food security, climate change, and economic disparities. By understanding these dynamics, readers will gain insight into how population trends influence global policies and individual lives.
As we navigate through the complexities of global population growth, we invite you to join us on this informative journey. Discover how different regions are responding to these challenges and what innovative solutions are being implemented to ensure a sustainable future. Stay with us as we unpack the critical issues surrounding population growth and its far-reaching effects on our planet and society.
As we approach 2024, the global population is projected to reach approximately 8 billion, marking a significant milestone in human history. This growth presents both opportunities and challenges that require careful consideration and strategic planning. Understanding the trends and implications of population growth is essential for policymakers, businesses, and communities worldwide.
Current Global Population Statistics
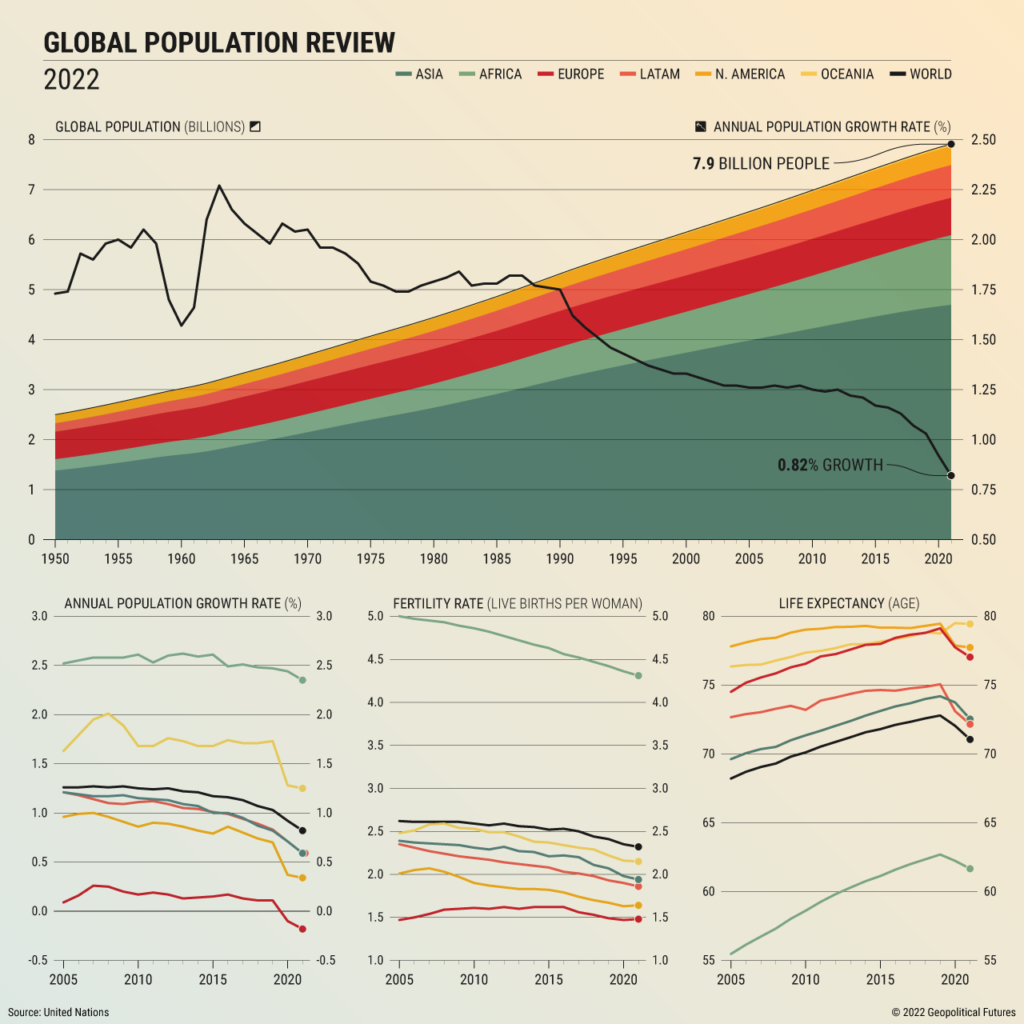
The current global population stands at around 7.9 billion, with projections indicating a rise to 8 billion by the end of 2024. This growth is not uniform across regions; while some areas, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, are experiencing rapid increases, others, such as Europe and parts of East Asia, are facing stagnation or decline. Understanding these statistics is crucial for addressing the diverse needs of different populations.
For instance, countries like Nigeria and India are expected to see significant population surges, which will impact resource allocation, urban planning, and social services. Conversely, nations with declining populations may face challenges related to labor shortages and aging demographics, necessitating different policy responses.
Factors Driving Population Growth
Several factors contribute to global population growth, including fertility rates, life expectancy, and migration patterns. High fertility rates in developing countries are often driven by cultural norms, lack of access to education, and limited family planning resources. In contrast, developed nations tend to have lower fertility rates due to increased access to education and career opportunities for women.
Additionally, advancements in healthcare have led to increased life expectancy, further contributing to population growth. As people live longer, the age structure of populations shifts, creating new challenges related to healthcare and social security systems. Migration also plays a significant role, as people move in search of better opportunities, impacting both the origin and destination countries.
Urbanization and Its Implications
Urbanization is a significant trend associated with population growth, with more than half of the world’s population now living in urban areas. This shift presents both opportunities and challenges, as cities become hubs of economic activity and innovation. However, rapid urbanization can lead to overcrowding, inadequate infrastructure, and increased demand for housing and services.
As urban populations grow, cities must adapt to meet the needs of their residents. This includes investing in sustainable transportation, affordable housing, and efficient public services. Failure to address these challenges can result in social unrest and decreased quality of life for urban dwellers.
Environmental Impact of Population Growth
The environmental implications of population growth are profound, as increased demand for resources leads to greater environmental degradation. Deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and climate change are all exacerbated by rising populations and consumption patterns. As more people inhabit the planet, the strain on natural resources intensifies, necessitating sustainable practices to mitigate these effects.
Addressing the environmental challenges associated with population growth requires a multifaceted approach, including promoting sustainable agriculture, reducing waste, and transitioning to renewable energy sources. Policymakers must prioritize environmental sustainability to ensure a livable planet for future generations.
Economic Challenges and Opportunities
Population growth presents both economic challenges and opportunities. On one hand, a growing population can lead to increased demand for goods and services, driving economic growth. On the other hand, if job creation does not keep pace with population growth, it can result in high unemployment rates and social unrest.
To harness the economic potential of a growing population, countries must invest in education and skills training to prepare the workforce for future job markets. Additionally, fostering entrepreneurship and innovation can create new economic opportunities, helping to alleviate poverty and improve living standards.
Health Implications of Population Growth
The health implications of population growth are significant, as increased population density can strain healthcare systems. Access to healthcare services may become limited, particularly in rapidly growing urban areas. This can lead to increased rates of communicable diseases, maternal and child mortality, and other health challenges.
To address these issues, governments must invest in healthcare infrastructure and ensure equitable access to services. Public health initiatives focused on education, vaccination, and preventive care are essential to improving health outcomes in growing populations.
Education and Gender Equality
Education plays a crucial role in managing population growth, particularly in empowering women and promoting gender equality. Access to education enables women to make informed choices about family planning and career
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Current Population | As of 2024, the global population is estimated to be around 8 billion, continuing a trend of significant growth over the past century. |
| Growth Rate | The global population growth rate has been declining, but it remains positive, with projections indicating an increase of approximately 1 billion people by 2030. |
| Regional Variations | Population growth is unevenly distributed, with regions like Sub-Saharan Africa experiencing rapid increases, while many developed countries face stagnation or decline. |
| Urbanization | More than half of the world’s population now lives in urban areas, leading to challenges in infrastructure, housing, and services. |
| Challenges | Key challenges include resource management, environmental sustainability, healthcare access, and economic opportunities for a growing population. |
| Policy Responses | Governments are implementing policies to address population growth, including family planning, education, and sustainable development initiatives. |
| Future Projections | By 2050, the global population is projected to reach around 9.7 billion, raising further concerns about food security, climate change, and social stability. |